Over-expression of Arabidopsis CAP causes decreased cell expansion leading to organ size reduction in transgenic tobacco plants
- PMID: 12646504
- PMCID: PMC4242246
- DOI: 10.1093/aob/mcg056
Over-expression of Arabidopsis CAP causes decreased cell expansion leading to organ size reduction in transgenic tobacco plants
Abstract
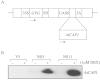
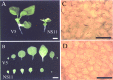
Cyclase-associated proteins (CAP) are multifunctional proteins involved in Ras-cAMP signalling and regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. It has recently been demonstrated that over-expression of AtCAP1 in transgenic arabidopsis plants causes severe morphological defects owing to loss of actin filaments. To test the generality of the function of AtCAP1 in plants, transgenic tobacco plants over-expressing an arabidopsis CAP (AtCAP1) under the regulation of a glucocorticoid-inducible promoter were produced. Over-expression of AtCAP1 in transgenic tobacco plants led to growth abnormalities, in particular a reduction in the size of leaves. Morphological alterations in leaves were the result of reduced elongation of epidermal and mesophyll cells.
Figures
References
-
- AoyamaT, Chua NH.1997. A glucocorticoid‐mediated transcription factor induction system in transgenic plants. The Plant Journal 11: 605–612. - PubMed
-
- BaluskaF, Jasik J, Edelmann HG, Salajová T, Volkmann D.2001. Latriculin B‐induced plant dwarfirsm: plant cell elongation is F‐actin‐dependent. Developmental Biology 231: 113–124. - PubMed
-
- BaumB, Li W, Perrimon N.2000. A cyclase‐associated protein regulates actin and cell polarity during Drosophila oogenesis and in yeast. Current Biology 10: 964–973. - PubMed
-
- BenlaliA, Draskovic I, Hazelett DJ, Treisman JE.2000. Act up controls actin polymerization to alter cell shape and restrict Hedgehog Signaling in the Drosophila eye disc. Cell 101: 271–281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

