Genetic and biological subgroups of low-stage follicular thyroid cancer
- PMID: 12651598
- PMCID: PMC1851238
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63902-8
Genetic and biological subgroups of low-stage follicular thyroid cancer
Abstract
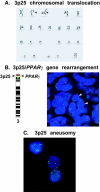
Investigations of cancer-specific gene rearrangements have increased our understanding of human neoplasia and led to the use of the rearrangements in pathological diagnosis of blood cell and connective tissue malignancies. Here, we have investigated 3p25 rearrangements of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma) gene in follicular epithelial tumors of the human thyroid gland. Eleven of 42 (26%) low-stage follicular carcinomas, 0 of 40 follicular adenomas, 1 of 30 Hurthle cell carcinomas, 1 of 90 papillary carcinomas, and 0 of 10 nodular goiters had 3p25 rearrangements by interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization. All 11 follicular carcinomas with 3p25 rearrangement exhibited strong, diffuse nuclear immunoreactivity for PPAR gamma, consistent with expression of PPAR gamma fusion protein. Twelve of 42 (29%) low-stage follicular carcinomas had 3p25 aneusomy without PPAR gamma rearrangement (P = 0.01), suggesting that PPAR gamma rearrangement and aneuploidy are independent early events in follicular cancer. Eleven of 12 follicular carcinomas with 3p25 aneusomy exhibited no PPAR gamma immunoreactivity, supporting the existence of two independent pathways. Follicular carcinoma patients with PPAR gamma rearrangement more frequently had vascular invasion (P = 0.01), areas of solid/nested tumor histology (P < 0.001), and previous non-thyroid cancers (P < 0.01) compared with follicular carcinoma patients without PPAR gamma rearrangement. Our experiments identify genetic subgroups of low-stage follicular thyroid cancer and provide evidence that follicular carcinomas with PPAR gamma rearrangement are a distinct biological entity. The findings support a model in which separate genetic alterations initiate distinct pathways of oncogenesis in thyroid carcinoma subtypes.
Figures

References
-
- Rowley JD: The critical role of chromosome translocations in human leukemias. Annu Rev Genet 1998, 32:495-519 - PubMed
-
- Mitelman F: Recurrent chromosome aberrations in cancer. Mutat Res 2000, 462:247-253 - PubMed
-
- Huettner CSS, Zhang P, Van Etten RA, Tenen DG: Reversibility of acute B-cell leukaemia induced by BCR-ABL1. Nat Genet 2000, 24:57-60 - PubMed
-
- Gorre ME, Mohammed M, Ellwood K, Hsu N, Paquette R, Rao PN, Sawyers CL: Clinical resistance to STI-571 cancer therapy caused by BCR-ABL gene mutation or amplification. Science 2001, 293:876-880 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

