The human Fn14 receptor gene is up-regulated in migrating glioma cells in vitro and overexpressed in advanced glial tumors
- PMID: 12651623
- PMCID: PMC1851233
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63927-2
The human Fn14 receptor gene is up-regulated in migrating glioma cells in vitro and overexpressed in advanced glial tumors
Abstract
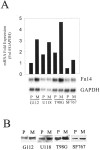
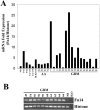
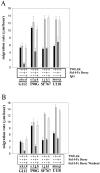
Glioblastoma multiforme comprises the majority of human brain tumors. Patients with glioblastoma multiforme have poor survival rates, with an average life expectancy of <1 year. To assess possible mechanisms and to potentially target invasive glioma cells, we previously measured the gene expression profiles of glioma cells under migration-activated or passive states. One of the genes identified was Fn14, which encodes a cell surface receptor for the tumor necrosis factor superfamily member named TWEAK. In this study, we show that Fn14 gene expression is induced in migration-activated glioma cells in vitro and significantly increases according to tumor grade in vivo (P < 0.01), with highest levels in glioblastoma tissue specimens. The in situ expression pattern of Fn14 mRNA and protein was confined to primary glioma cells and the vascular endothelium, with no detection in adjacent normal brain. Conversely, TWEAK mRNA levels are low in glioblastoma samples relative to normal brain tissue. In addition, activation of the Fn14 receptor by addition of recombinant TWEAK resulted in increased glioma cell migration in vitro. These results suggest a positive role for TWEAK and Fn14 in glioma progression and indicate that Fn14 gene expression may serve as a marker for invasive glioma cells.
Figures

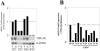
References
-
- Giese A, Westphal M: Glioma invasion in the central nervous system. Neurosurgery 1996, 39:235-250 - PubMed
-
- Pilkington GJ: Tumour cell migration in the central nervous system. Brain Pathol 1994, 4:157-166 - PubMed
-
- Davis FG, McCarthy BJ: Epidemiology of brain tumors. Curr Opin Neurol 2000, 13:635-640 - PubMed
-
- Mornex F, Nayel H, Taillandier L: Radiation therapy for malignant astrocytomas in adults. Radiother Oncol 1993, 27:181-192 - PubMed
-
- Vick NA, Paleologos NA: External beam radiotherapy: hard facts and painful realities. J Neurooncol 1995, 24:93-95 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

