Distinct roles of dopamine D2L and D2S receptor isoforms in the regulation of protein phosphorylation at presynaptic and postsynaptic sites
- PMID: 12651945
- PMCID: PMC153088
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0730708100
Distinct roles of dopamine D2L and D2S receptor isoforms in the regulation of protein phosphorylation at presynaptic and postsynaptic sites
Abstract
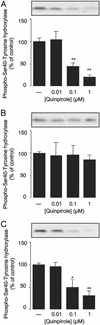
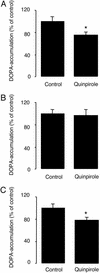
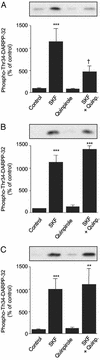
Dopamine D2 receptors are highly expressed in the dorsal striatum where they participate in the regulation of (i) tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), in nigrostriatal nerve terminals, and (ii) the dopamine- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein of 32 kDa (DARPP-32), in medium spiny neurons. Two isoforms of the D2 receptor are generated by differential splicing of the same gene and are referred to as short (D2S) and long (D2L) dopamine receptors. Here we have used wild-type mice, dopamine D2 receptor knockout mice (D2 KO mice; lacking both D2S and D2L receptors) and D2L receptor-selective knockout mice (D2L KO mice) to evaluate the involvement of each isoform in the regulation of the phosphorylation of TH and DARPP-32. Incubation of striatal slices from wild-type mice with quinpirole, a dopamine D2 receptor agonist, decreased the state of phosphorylation of TH at Ser-40 and its enzymatic activity. Both effects were abolished in D2 KO mice but were still present in D2L KO mice. In wild-type mice, quinpirole inhibits the increase in DARPP-32 phosphorylation at Thr-34 induced by SKF81297, a dopamine D1 receptor agonist. This effect is absent in D2 KO as well as D2L KO mice. The inability of quinpirole to regulate DARPP-32 phosphorylation in D2L KO mice cannot be attributed to decreased coupling of D2S receptors to G proteins, because quinpirole produces a similar stimulation of [(35)S]GTPgammaS binding in wild-type and D2L KO mice. These results demonstrate that D2S and D2L receptors participate in presynaptic and postsynaptic dopaminergic transmission, respectively.
Figures
References
-
- Gingrich J A, Caron M G. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1993;16:299–321. - PubMed
-
- Civelli O, Bunzow J R, Grandy D K. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1993;32:281–307. - PubMed
-
- Picetti R, Saiardi A, Samad T A, Bozzi Y, Baik J-H, Borrelli E. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1997;11:121–142. - PubMed
-
- Kebabian J W, Calne D B. Nature. 1979;277:93–96. - PubMed
-
- Stoof J C, Kebabian J W. Nature. 1981;294:366–368. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

