Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of [(14)C]ribavirin in rats and cynomolgus monkeys
- PMID: 12654676
- PMCID: PMC152481
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.4.1395-1398.2003
Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of [(14)C]ribavirin in rats and cynomolgus monkeys
Abstract
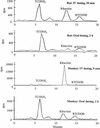
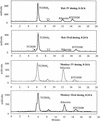
Absorption, pharmacokinetics, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of [(14)C]ribavirin were studied in rats (30 mg/kg of body weight) and cynomolgus monkeys (10 mg/kg) after intravenous (i.v.) and oral administration. The oral absorption and bioavailability were 83 and 59%, respectively, in rats and 87 and 55%, respectively, in monkeys. After i.v. administration, the elimination half-life (t([1/2])) was 9.9 h in rats and 130 h in monkeys and the total body clearance was 2,600 ml/h/kg in rats and 224 ml/h/kg in monkeys. The apparent volume of distribution was 11.4 liter/kg in rats and 29.4 liter/kg in monkeys. There was extensive distribution of drug-derived radioactivity into red blood cells and extensive metabolism of ribavirin in rats and a lesser degree of metabolism in monkeys. Excretion of total radioactivity in urine from rats accounted for 84% of the i.v. dose and 83% of the oral dose, whereas that from monkeys accounted for 47% of the i.v. dose and 67% of the oral dose. Several metabolites were observed in plasma and urine from both species. The amount of unchanged ribavirin in urine from both species was quite small after either i.v. or oral administration.
Figures
References
-
- Catlin, D. H., R. Smith, and A. I. Samuels. 1980. 14C-ribavirin: distribution and pharmacokinetic studies in rats, baboon and man, p. 83-98. In R. A. Smith and W. Kirkpatrick (ed.), Ribavirin: a broad spectrum antiviral agent. Academic Press, New York, N.Y.
-
- Laskin, O. L., J. A. Longstreth, C. C. Hart, D. Scavuzzo, C. M. Kalman, J. D. Connor, and R. B. Roberts. 1987. Ribavirin disposition in high-risk patients for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 41:546-555. - PubMed
-
- Miller, J. P., L. J. Kigwana, D. G. Streeter, R. K. Robins, L. N. Simon, and J. Roboz. 1977. The relationship between the metabolism of ribavirin and its proposed mechanism of action. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 284:211-229. - PubMed
-
- Page, T., and J. D. Conner. 1990. The metabolism of ribavirin in erythrocytes and nucleated cells. Intl. J. Biochem. 22:379-383. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources