In vitro metronidazole and tinidazole activities against metronidazole-resistant strains of Trichomonas vaginalis
- PMID: 12654679
- PMCID: PMC152533
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.4.1407-1409.2003
In vitro metronidazole and tinidazole activities against metronidazole-resistant strains of Trichomonas vaginalis
Abstract
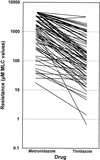
The in vitro activities of tinidazole and metronidazole against Trichomonas vaginalis isolates clinically resistant to metronidazole were compared. Minimal lethal concentrations (MLCs) of tinidazole were significantly lower than MLCs of metronidazole. Increased metronidazole resistance correlated with increased tinidazole resistance. These data support a role for tinidazole in the treatment of trichomoniasis.
Figures

References
-
- Bowden, F. J., and G. P. Garnett. 1999. Why is Trichomonas vaginalis ignored? Sex. Transm. Infect. 75:372-374. - PubMed
-
- Cates, W., Jr. 1999. Estimates of the incidence and prevalence of sexually transmitted diseases in the United States. Sex. Transm. Dis. 26(Suppl.):S2-S7. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1993. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 42(RR-14):70-72.
-
- Cotch, M. F., J. G. Pastorek II, R. P. Nugent, S. L. Hillier, R. S. Gibbs, D. H. Martin, D. A. Eschenbach, R. Edelman, J. C. Carey, J. A. Regan, M. A. Krohn, M. A. Klebanoff, A. V. Rao, and G. G. Rhoads. 1997. Trichomonas vaginalis associated with low birth weight and preterm delivery. Sex. Transm. Dis. 24:353-360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

