Efficacy of micafungin alone or in combination against systemic murine aspergillosis
- PMID: 12654692
- PMCID: PMC152509
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.4.1452-1455.2003
Efficacy of micafungin alone or in combination against systemic murine aspergillosis
Abstract
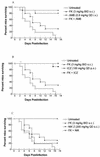
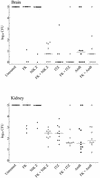
We tested the efficacy of micafungin (FK) alone or in combination with other antifungals against systemic murine aspergillosis. FK alone at 10 mg/kg of body weight/dose prolonged survival (P = 0.01) and reduced CFU in the brain and kidney. Combination therapy that used suboptimal FK with amphotericin B or itraconazole prolonged survival. Although no survivors were free of infection, no antagonism was seen. Nikkomycin Z with FK showed significantly greater potency (P < 0.01) than either alone.
Figures

References
-
- Chiou, C. C., N. Mavrogiorgos, E. Tillem, R. Hector, and T. J. Walsh. 2001. Synergy, pharmacodynamics, and time-sequenced ultrastructural changes of the interaction between nikkomycin Z and the echinocandin FK463 against Aspergillus fumigatus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 45:3310-3321. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Denning, D. W. 1998. Invasive aspergillosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 26:781-803. - PubMed
-
- Denning, D. W. 1994. Treatment of invasive aspergillosis. J. Infect. 28(Suppl. 1):25-33. - PubMed
-
- Denning, D. W., and D. A. Stevens. 1990. Antifungal and surgical treatment of invasive aspergillosis: review of 2,121 published cases. Rev. Infect. Dis. 12:1147-1201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

