Critical role of oxidative stress in estrogen-induced carcinogenesis
- PMID: 12655060
- PMCID: PMC153022
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0437929100
Critical role of oxidative stress in estrogen-induced carcinogenesis
Abstract
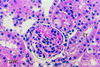
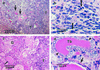
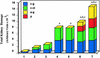
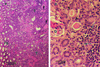
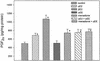
Mechanisms of estrogen-induced tumorigenesis in the target organ are not well understood. It has been suggested that oxidative stress resulting from metabolic activation of carcinogenic estrogens plays a critical role in estrogen-induced carcinogenesis. We tested this hypothesis by using an estrogen-induced hamster renal tumor model, a well established animal model of hormonal carcinogenesis. Hamsters were implanted with 17beta-estradiol (betaE2), 17alpha-estradiol (alphaE2), 17alpha-ethinylestradiol (alphaEE), menadione, a combination of alphaE2 and alphaEE, or a combination of alphaEE and menadione for 7 months. The group treated with betaE2 developed target organ specific kidney tumors. The kidneys of hamsters treated with alphaE2, alphaEE, or menadione alone did not show any gross evidence of tumor. Kidneys of hamsters treated with a combination of alphaE2 and alphaEE showed early signs of proliferation in the interstitial cells. Kidneys of hamsters treated with a combination of menadione and alphaEE showed foci of tumor with congested tubules and atrophic glomeruli. betaE2-treated tumor-bearing kidneys showed >2-fold increase in 8-iso-prostaglandin F(2alpha) (8-iso-PGF(2alpha)) levels compared with untreated controls. Kidneys of hamsters treated with a combination of menadione and alphaEE showed increased 8-iso-PGF(2alpha) levels compared with untreated controls, whereas no increase in 8-iso-PGF(2alpha) was detected in kidneys of alphaEE-treated group. A chemical known to produce oxidative stress or a potent estrogen with poor ability to produce oxidative stress, were nontumorigenic in hamsters, when given as single agents, but induced renal tumors, when given together. Thus, these data provide evidence that oxidant stress plays a crucial role in estrogen-induced carcinogenesis.
Figures

References
-
- Henderson B E, Feigelson H S. Carcinogenesis. 2000;21:427–433. - PubMed
-
- Ross R K, Paganini-Hill A, Wan P C, Pike M C. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92:328–332. - PubMed
-
- Key T J. Endocrine-Related Cancer. 1999;6:175–180. - PubMed
-
- Verloop J, Rookus M A, Van Leeuwen F E. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1838–1839. - PubMed
-
- Rossouw J E, Anderson G L, Prentice R L, LaCroix A Z, Kooperberg C, Stefanick M L, Jackson R D, Beresford S A, Howard B V, Johnson K C, Kotchen J M, Ockene J. J Am Med Assoc. 2002;288:321–333. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

