Effect of paracetamol (acetaminophen) and ibuprofen on body temperature in acute ischemic stroke PISA, a phase II double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial [ISRCTN98608690]
- PMID: 12657165
- PMCID: PMC152640
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2261-3-2
Effect of paracetamol (acetaminophen) and ibuprofen on body temperature in acute ischemic stroke PISA, a phase II double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial [ISRCTN98608690]
Abstract
Background: Body temperature is a strong predictor of outcome in acute stroke. In a previous randomized trial we observed that treatment with high-dose acetaminophen (paracetamol) led to a reduction of body temperature in patients with acute ischemic stroke, even when they had no fever. The purpose of the present trial was to study whether this effect of acetaminophen could be reproduced, and whether ibuprofen would have a similar, or even stronger effect.
Methods: Seventy-five patients with acute ischemic stroke confined to the anterior circulation were randomized to treatment with either 1000 mg acetaminophen, 400 mg ibuprofen, or placebo, given 6 times daily during 5 days. Treatment was started within 24 hours from the onset of symptoms. Body temperatures were measured at 2-hour intervals during the first 24 hours, and at 6-hour intervals thereafter.
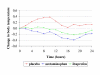
Results: No difference in body temperature at 24 hours was observed between the three treatment groups. However, treatment with high-dose acetaminophen resulted in a 0.3 degrees C larger reduction in body temperature from baseline than placebo treatment (95% CI: 0.0 to 0.6 degrees C). Acetaminophen had no significant effect on body temperature during the subsequent four days compared to placebo, and ibuprofen had no statistically significant effect on body temperature during the entire study period.
Conclusions: Treatment with a daily dose of 6000 mg acetaminophen results in a small, but potentially worthwhile decrease in body temperature after acute ischemic stroke, even in normothermic and subfebrile patients. Further large randomized clinical trials are needed to study whether early reduction of body temperature leads to improved outcome.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PISA. The effect of paracetamol (acetaminophen) and ibuprofen on body temperature in acute stroke: protocol for a phase II double-blind randomised placebo-controlled trial [ISRCTN98608690].BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2002 Mar 27;2:7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2261-2-7. Epub 2002 Mar 27. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2002. PMID: 11918829 Free PMC article.
-
Aspirin compared with acetaminophen in the treatment of fever and other symptoms of upper respiratory tract infection in adults: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, single-dose, 6-hour dose-ranging study.Clin Ther. 2005 Jul;27(7):993-1003. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2005.06.002. Clin Ther. 2005. PMID: 16154478 Clinical Trial.
-
[Treatment of stroke by reducing the body temperature; 'Paracetamol (acetaminophen) in stroke' (PAIS): start of a clinical trial].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2003 Oct 4;147(40):1976-8. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2003. PMID: 14574783 Clinical Trial. Dutch.
-
Efficacy and safety of ibuprofen and acetaminophen in children and adults: a meta-analysis and qualitative review.Ann Pharmacother. 2010 Mar;44(3):489-506. doi: 10.1345/aph.1M332. Epub 2010 Feb 11. Ann Pharmacother. 2010. PMID: 20150507 Review.
-
Alternating acetaminophen and ibuprofen in the febrile child: examination of the evidence regarding efficacy and safety.Pediatr Nurs. 2003 Sep-Oct;29(5):379-82. Pediatr Nurs. 2003. PMID: 14651311 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Hibernation, Hypothermia and a Possible Therapeutic "Shifted Homeostasis" Induced by Central Activation of A1 Adenosine Receptor (A1AR).Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2016 Apr;36(2):51-4. Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2016. PMID: 27333659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted Temperature Management for Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Literature Review.J Clin Med. 2024 Jan 19;13(2):586. doi: 10.3390/jcm13020586. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38276093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paracetamol sharpens reflection and spatial memory: a double-blind randomized controlled study in healthy volunteers.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016 Dec 5;10:3969-3976. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S111590. eCollection 2016. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016. PMID: 27980393 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A review on targeted temperature management for cardiac arrest and traumatic brain injury.Front Neurosci. 2024 Oct 31;18:1397300. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1397300. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39544908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Temperature Management With Paracetamol in Acute Stroke Patients: Evidence From Randomized Controlled Trials.Front Neurol. 2018 Nov 20;9:917. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00917. eCollection 2018. Front Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30515128 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Przelomski MM, Roth RM, Gleckman RA, Marcus EM. Fever in the wake of a stroke. Neurology. 1986;36:427–429. - PubMed
-
- Castillo J, Martinez F, Leira R, Prieto JM, Lema M, Noya M. Mortality and morbidity of acute cerebral infarction related to temperature and basal analytic parameters. Cerebrovasc Dis. 1994;4:66–71.
-
- Azzimondi G, Bassein L, Nonino F, Fiorani L, Vignatelli L, Re G, et al. Fever in acute stroke worsens prognosis. A prospective study. Stroke. 1995;26:2040–2043. - PubMed
-
- Hindfelt B. The prognostic significance of subfebrility and fever in ischaemic cerebral infarction. Acta Neurol Scand. 1976;53:72–79. - PubMed
-
- Castillo J, Davalos A, Marrugat J, Noya M. Timing for fever-related brain damage in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 1998;29:2455–2460. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical