Rapid changes in shape and number of MHC class II expressing cells in rat airways after Mycoplasma pulmonis infection
- PMID: 12657245
- PMCID: PMC7124235
- DOI: 10.1016/s0008-8749(03)00026-1
Rapid changes in shape and number of MHC class II expressing cells in rat airways after Mycoplasma pulmonis infection
Abstract
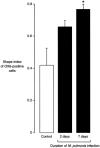
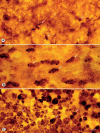
Mycoplasma pulmonis infection in rodents causes a chronic inflammatory airway disease with a strong immunological component, leading to mucosal remodeling and angiogenesis. We sought to determine the effect of this infection on the shape and number of dendritic cells and other major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II expressing cells in the airway mucosa of Wistar rats. Changes in the shape of subepithelial OX6 (anti-MHC class II)-immunoreactive cells were evident in the tracheal mucosa 2 days after intranasal inoculation with M. pulmonis. By 1 week, the shape of the cells had changed from stellate to rounded (mean shape index increased from 0.42 to 0.77). The number of OX6-positive cells was increased 6-fold at 1 week and 16-fold at 4 weeks. Coincident with these changes, many columnar epithelial cells developed OX6 immunoreactivity, which was still present at 4 weeks. We conclude that M. pulmonis infection creates a potent immunologic stimulus that augments and transforms the OX6-immunoreactive cell population in the airways by changing the functional state of airway dendritic cells, initiating an influx of MHC class II expressing cells, and activating expression of MHC class II molecules by airway epithelial cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Development of the airway intraepithelial dendritic cell network in the rat from class II major histocompatibility (Ia)-negative precursors: differential regulation of Ia expression at different levels of the respiratory tract.J Exp Med. 1994 Jan 1;179(1):203-12. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.1.203. J Exp Med. 1994. PMID: 8270865 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoglobulin class- and subclass-specific responses to Mycoplasma pulmonis in sera and secretions of naturally infected Sprague-Dawley female rats.Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2181-5. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2181-2185.1991. Infect Immun. 1991. PMID: 2037378 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis of dendritic cells in the rat tracheal mucosa.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1998 Oct;19(4):598-605. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.19.4.2870. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1998. PMID: 9761756
-
Mycoplasma pulmonis-host relationships in a breeding colony of Sprague-Dawley rats with enzootic murine respiratory mycoplasmosis.Lab Anim Sci. 1985 Dec;35(6):597-608. Lab Anim Sci. 1985. PMID: 3912611 Review.
-
Bacterial antigen delivery systems: phagocytic processing of bacterial antigens for MHC-I and MHC-II presentation to T cells.Behring Inst Mitt. 1997 Feb;(98):197-211. Behring Inst Mitt. 1997. PMID: 9382741 Review.
Cited by
-
Intranasal exposure to bacterial superantigens induces airway inflammation in HLA class II transgenic mice.Infect Immun. 2006 Feb;74(2):1284-96. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.2.1284-1296.2006. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16428778 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular Microbiology of Mycoplasma canis.Infect Immun. 2016 May 24;84(6):1785-1795. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01440-15. Print 2016 Jun. Infect Immun. 2016. PMID: 27045036 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steinman R.M. The dendritic cell system and its role in immunogenicity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1991;9:271–296. - PubMed
-
- Holt P.G., Schon-Hegrad M.A., Oliver J., Holt B.J., McMenamin P.G. A contiguous network of dendritic antigen-presenting cells within the respiratory epithelium. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol. 1990;91:155–159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

