GABA(B) receptors inhibit dendrodendritic transmission in the rat olfactory bulb
- PMID: 12657661
- PMCID: PMC6742016
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-06-02032.2003
GABA(B) receptors inhibit dendrodendritic transmission in the rat olfactory bulb
Abstract
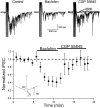
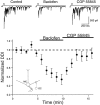
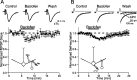
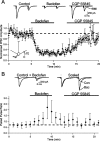
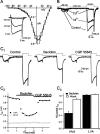
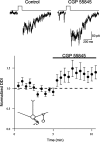
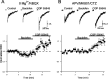
In the mammalian olfactory bulb, mitral cell dendrites release glutamate onto the dendritic spines of granule cells, which in turn release GABA back onto mitral dendrites. This local synaptic circuit forms the basis for reciprocal dendrodendritic inhibition mediated by ionotropic GABA(A) receptors in mitral cells. Surprisingly little is known about neurotransmitter modulation of dendrodendritic signaling in the olfactory bulb. In this study, we examine whether metabotropic GABA(B) receptors modulate dendrodendritic signaling between mitral and granule cells. We find that the selective GABA(B) agonist baclofen reduces mitral cell recurrent inhibition mediated by dendrodendritic synapses. GABA(B) receptor activation causes only a weak inhibition of field EPSCs in the external plexiform layer and only slightly reduces glutamate-mediated mitral cell self-excitation. Although GABA(B) receptors depress mitral cell glutamate release only weakly, baclofen causes a marked reduction in the amplitude of granule-cell-evoked, GABA(A)-mediated IPSCs in mitral cells. In addition to reducing the amplitude of granule-cell-evoked IPSCs, baclofen causes a change from paired-pulse depression to paired-pulse facilitation, suggesting that GABA(B) receptors modulate GABA release from granule cells. To explore the mechanism of action of GABA(B) receptors further, we show that baclofen inhibits high-voltage-activated calcium currents in granule cells. Together, these findings suggest that GABA(B) receptors modulate dendrodendritic inhibition primarily by inhibiting granule cell calcium channels and reducing the release of GABA. Furthermore, we show that endogenous GABA regulates the strength of dendrodendritic inhibition via the activation of GABA(B) autoreceptors.
Figures
References
-
- Aroniadou-Anderjaska V, Ennis M, Shipley MT. Current-source density analysis in the rat olfactory bulb: laminar distribution of kainate/AMPA- and NMDA-receptor-mediated currents. J Neurophysiol. 1999;81:15–28. - PubMed
-
- Aroniadou-Anderjaska V, Zhou FM, Priest CA, Ennis M, Shipley MT. Tonic and synaptically evoked presynaptic inhibition of sensory input to the rat olfactory bulb via GABA(B) heteroreceptors. J Neurophysiol. 2000;84:1194–1203. - PubMed
-
- Bean BP. Neurotransmitter inhibition of neuronal calcium currents by changes in channel voltage dependence. Nature. 1989;340:153–156. - PubMed
-
- Brenowitz S, David J, Trussell L. Enhancement of synaptic efficacy by presynaptic GABA(B) receptors. Neuron. 1998;20:135–141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
