Neuronal glutamate uptake Contributes to GABA synthesis and inhibitory synaptic strength
- PMID: 12657662
- PMCID: PMC6742021
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-06-02040.2003
Neuronal glutamate uptake Contributes to GABA synthesis and inhibitory synaptic strength
Abstract
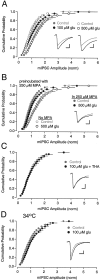
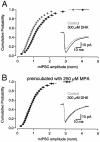
Neurons must maintain a supply of neurotransmitter in their presynaptic terminals to fill synaptic vesicles. GABA is taken up into inhibitory terminals by transporters or is synthesized from glutamate by glutamic acid decarboxylase. Here we report that glutamate transporters supply GABAergic terminals in the hippocampus with glutamate, which is then used to synthesize GABA for filling synaptic vesicles. Glutamate transporter antagonists reduced IPSC and miniature IPSC (mIPSC) amplitudes, consistent with a reduction in the amount of GABA packaged into each synaptic vesicle. This reduction occurred rapidly and independently of synaptic activity, suggesting that modulation of vesicular GABA content does not require vesicle release and refilling. Raising extracellular glutamate levels increased mIPSC amplitudes by enhancing glutamate uptake and, consequently, GABA synthesis. These results indicate that neuronal glutamate transporters strengthen inhibitory synapses in response to extracellular glutamate. This modulation appears to occur under normal conditions and may constitute a negative feedback mechanism to combat hyperexcitability.
Figures
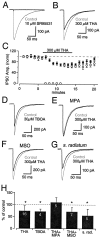
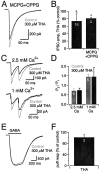
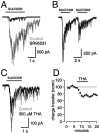
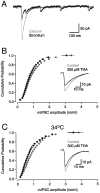
References
-
- Arnth-Jensen N, Jaboudon D, Scanziani M. Cooperation between independent hippocampal synapses is controlled by glutamate uptake. Nat Neurosci. 2002;5:325–331. - PubMed
-
- Asztely F, Erdemli G, Kullmann DM. Extrasynaptic glutamate spillover in the hippocampus: dependence on temperature and the role of active glutamate uptake. Neuron. 1997;18:281–293. - PubMed
-
- Bergles DE, Jahr CE. Synaptic activation of glutamate transporters in hippocampal astrocytes. Neuron. 1997;19:1297–1308. - PubMed
-
- Brasnjo G, Otis TS. Neuronal glutamate transporters control activation of postsynaptic metabotropic glutamate receptors and influence cerebellar long-term depression. Neuron. 2001;31:607–616. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
