Neurotrophin-regulated sorting of opioid receptors in the biosynthetic pathway of neurosecretory cells
- PMID: 12657666
- PMCID: PMC6742051
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-06-02075.2003
Neurotrophin-regulated sorting of opioid receptors in the biosynthetic pathway of neurosecretory cells
Abstract
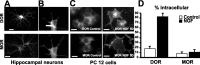
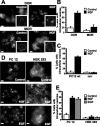
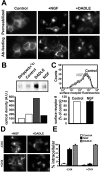
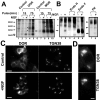
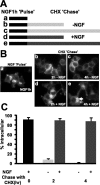
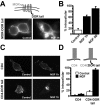
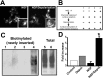
Neurotrophins modulate the endogenous opioid system, but the underlying mechanisms are poorly understood. We observed an unexpected effect of neurotrophin signaling on the membrane trafficking of recombinant opioid receptors expressed in neurosecretory cells. Epitope-tagged delta opioid receptor (DOR) and mu opioid receptor (MOR) were differentially localized between surface and internal membrane pools, respectively, when expressed in primary cultured hippocampal neurons, consistent with previous studies by others of natively expressing neurons. Selective intracellular targeting of DOR was observed in nerve growth factor (NGF)-differentiated PC12 neurosecretory cells but not in PC12 cells cultured in the absence of NGF, where both DOR and MOR were localized in the plasma membrane. Surprisingly, NGF initiated intracellular targeting of DOR in PC12 cells acutely, within 60 min after initial activation of TrkA. The NGF-induced intracellular pool of DOR originated from a late stage of the biosynthetic pathway after exit from the endoplasmic reticulum and processing of N-linked glycans in the Golgi, resulting in the accumulation in cells of a biochemically mature "reserve" pool of intracellular DOR that exhibited depolarization-dependent insertion into the plasma membrane. The C-terminal cytoplasmic tail of DOR contains a signal determining the specificity of NGF-regulated intracellular targeting. These results indicate that cloned opioid receptors are differentially targeted when expressed heterologously in neurosecretory cells, establish a model system that facilitates mechanistic study of this process, and suggest a novel function of neurotrophins in modulating the anterograde membrane trafficking of opioid receptors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Morphine acutely regulates opioid receptor trafficking selectively in dendrites of nucleus accumbens neurons.J Neurosci. 2003 May 15;23(10):4324-32. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-10-04324.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12764121 Free PMC article.
-
Heteromerization of the μ- and δ-opioid receptors produces ligand-biased antagonism and alters μ-receptor trafficking.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Jun;337(3):868-75. doi: 10.1124/jpet.111.179093. Epub 2011 Mar 21. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011. PMID: 21422164 Free PMC article.
-
Dual RXR motifs regulate nerve growth factor-mediated intracellular retention of the delta opioid receptor.Mol Biol Cell. 2019 Mar 1;30(5):680-690. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E18-05-0292. Epub 2019 Jan 2. Mol Biol Cell. 2019. PMID: 30601694 Free PMC article.
-
Mu and delta opioid receptor immunoreactivity and mu receptor regulation in brainstem cells cultured from late fetal and early postnatal rats.Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 2004 Mar 22;149(1):9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.devbrainres.2003.11.012. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 15013624
-
TRP Channel Trafficking.In: Liedtke WB, Heller S, editors. TRP Ion Channel Function in Sensory Transduction and Cellular Signaling Cascades. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2007. Chapter 23. In: Liedtke WB, Heller S, editors. TRP Ion Channel Function in Sensory Transduction and Cellular Signaling Cascades. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2007. Chapter 23. PMID: 21204515 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential noxious and motor tolerance of chronic delta opioid receptor agonists in rodents.Neuroscience. 2009 Jun 30;161(2):381-91. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.03.053. Epub 2009 Mar 27. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19328839 Free PMC article.
-
Forebrain delta opioid receptors regulate the response of delta agonist in models of migraine and opioid-induced hyperalgesia.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 19;10(1):17629. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-74605-9. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33077757 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo trafficking of endogenous opioid receptors.Life Sci. 2008 Nov 21;83(21-22):693-9. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2008.09.023. Epub 2008 Oct 5. Life Sci. 2008. PMID: 18930741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nerve growth factor-regulated emergence of functional delta-opioid receptors.J Neurosci. 2010 Apr 21;30(16):5617-28. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5296-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20410114 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of the mu-opioid receptor with GPR177 (Wntless) inhibits Wnt secretion: potential implications for opioid dependence.BMC Neurosci. 2010 Mar 9;11:33. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-11-33. BMC Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20214800 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beattie EC, Stellwagen D, Morishita W, Bresnahan JC, Ha BK, Von Zastrow M, Beattie MS, Malenka RC. Control of synaptic strength by glial TNFalpha. Science. 2002;295:2282–2285. - PubMed
-
- Beczkowska IW, Gracy KN, Pickel VM, Inturrisi CE. Detection of delta opioid receptor and N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor-like immunoreactivity in retinoic acid-differentiated neuroblastoma x glioma (NG108–15) cells. J Neurosci Res. 1997;47:83–89. - PubMed
-
- Cao TT, Mays RW, von Zastrow M. Regulated endocytosis of G protein-coupled receptors by a biochemically and functionally distinct subpopulation of clathrin-coated pits. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:24592–24602. - PubMed
-
- Cao TT, Deacon HW, Reczek D, Bretscher A, von Zastrow M. A kinase-regulated PDZ-domain interaction controls endocytic sorting of the beta2-adrenergic receptor. Nature. 1999;401:286–290. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
