Absence of Whisker-related pattern formation in mice with NMDA receptors lacking coincidence detection properties and calcium signaling
- PMID: 12657691
- PMCID: PMC6742004
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-06-02323.2003
Absence of Whisker-related pattern formation in mice with NMDA receptors lacking coincidence detection properties and calcium signaling
Abstract
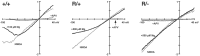
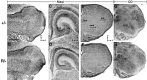
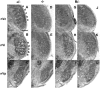
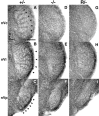
Precise refinement of synaptic connectivity is the result of activity-dependent mechanisms in which coincidence-dependent calcium signaling by NMDA receptors (NMDARs) under control of the voltage-dependent Mg2+ block might play a special role. In the developing rodent trigeminal system, the pattern of synaptic connections between whisker-specific inputs and their target cells in the brainstem is refined to form functionally and morphologically distinct units (barrelettes). To test the role of NMDA receptor signaling in this process, we introduced the N598R mutation into the native NR1 gene. This leads to the expression of functional NMDARs that are Mg2+ insensitive and Ca2+ impermeable. Newborn mice expressing exclusively NR1 N598R-containing NMDARs do not show any whisker-related patterning in the brainstem, whereas the topographic projection of trigeminal afferents and gross brain morphology appear normal. Furthermore, the NR1 N598R mutation does not affect expression levels of NMDAR subunits and other important neurotransmitter receptors. Our results show that coincidence detection by, and/or Ca2+ permeability of, NMDARs is necessary for the development of somatotopic maps in the brainstem and suggest that highly specific signaling underlies synaptic refinement.
Figures




References
-
- Bayer KU, Schulman H. Regulation of signal transduction by protein targeting: the case for CaMKII. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;289:917–923. - PubMed
-
- Behe P, Stern P, Wyllie DJ, Nassar M, Schoepfer R, Colquhoun D. Determination of NMDA NR1 subunit copy number in recombinant NMDA receptors. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1995;262:205–213. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari Y. Developing networks play a similar melody. Trends Neurosci. 2001;24:353–360. - PubMed
-
- Bliss TV, Collingridge GL. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993;361:31–39. - PubMed
-
- Bourne HR, Nicoll R. Molecular machines integrate coincident synaptic signals. Cell [Suppl] 1993;72:65–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
