Regulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase by cannabinoids in hippocampus
- PMID: 12657697
- PMCID: PMC6742049
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-06-02371.2003
Regulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase by cannabinoids in hippocampus
Abstract
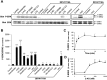
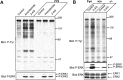
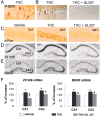
Endocannabinoids form a novel class of intercellular messengers, the functions of which include retrograde signaling in the brain and mediation or modulation of several types of synaptic plasticity. Yet, the signaling mechanisms and long-term effects of the stimulation of CB1 cannabinoid receptors (CB1-R) are poorly understood. We show that anandamide, 2-arachidonoyl-glycerol, and Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) in hippocampal slices. In living mice, THC activated ERK in hippocampal neurons and induced its accumulation in the nuclei of pyramidal cells in CA1 and CA3. Both effects were attributable to stimulation of CB1-R and activation of MAP kinase/ERK kinase (MEK). In hippocampal slices, the stimulation of ERK was independent of phosphatidyl-inositol-3-kinase but was regulated by cAMP. The endocannabinoid-induced stimulation of ERK was lost in Fyn knock-out mice, in slices and in vivo, although it was insensitive to inhibitors of Src-family tyrosine kinases in vitro, suggesting a noncatalytic role of Fyn. Finally, the effects of cannabinoids on ERK activation were dependent on the activity of glutamate NMDA receptors in vivo, but not in hippocampal slices, indicating the existence of several pathways linking CB1-R to the ERK cascade. In vivo THC induced the expression of immediate-early genes products (c-Fos protein, Zif268, and BDNF mRNAs), and this induction was prevented by an inhibitor of MEK. The strong potential of cannabinoids for inducing long-term alterations in hippocampal neurons through the activation of the ERK pathway may be important for the physiological control of synaptic plasticity and for the general effects of THC in the context of drug abuse.
Figures




References
-
- Alessi DR, Cuenda A, Cohen P, Dudley DT, Saltiel AR. PD 098059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:27489–27494. - PubMed
-
- Al-Hayani A, Wease KN, Ross RA, Pertwee RG, Davies SN. The endogenous cannabinoid anandamide activates vanilloid receptors in the rat hippocampal slice. Neuropharmacology. 2001;41:1000–1005. - PubMed
-
- Atkins CM, Selcher JC, Petraitis JJ, Trzaskos JM, Sweatt JD. The MAPK cascade is required for mammalian associative learning. Nat Neurosci. 1998;1:602–609. - PubMed
-
- Barnett G, Licko V, Thompson T. Behavioral pharmacokinetics of marijuana. Psychopharmacology. 1985;85:51–56. - PubMed
-
- Bidaut-Russell M, Devane WA, Howlett AC. Cannabinoid receptors and modulation of cyclic AMP accumulation in the rat brain. J Neurochem. 1990;55:21–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
