Adjuvant-dependent modulation of Th1 and Th2 responses to immunization with beta-amyloid
- PMID: 12663680
- PMCID: PMC1483061
- DOI: 10.1093/intimm/dxg049
Adjuvant-dependent modulation of Th1 and Th2 responses to immunization with beta-amyloid
Abstract
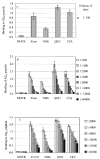
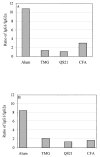
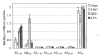
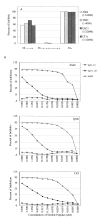
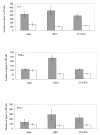
The role of adjuvant on the T(h)1 and T(h)2 immune responses to Abeta-immunotherapy (Abeta(42 )peptide) was examined in wild-type mice. Fine epitope analysis with overlapping oligomers of the Abeta(42) sequence identified the 1-15 region as a dominant B cell epitope. The 6-20 peptide was recognized only weakly by antisera from mice administrated with Abeta(42) peptide formulated in complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA), alum or TiterMax Gold (TMG). However, mice immunized with Abeta(42) mixed with QS21 induced a significant antibody response to the 6-20 peptide. The only T cell epitope found was within the 6-28 sequence of Abeta(42). QS21 and CFA induced the strongest humoral response to Abeta, alum was intermediate, and TMG the weakest adjuvant. Analysis of antibody isotypes specific for Abeta indicates that alum induces primarily T(h)2-type immune response, whereas TMG, CFA and QS21 shift the immune responses toward a T(h)1 phenotype. Stimulation of splenocytes from Abeta-immunized mice with Abeta(40) peptide induced strikingly different cytokine expression profiles. QS21 and CFA induced significant IFN-gamma, IL-4 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression, whereas alum induced primarily IL-4 production. As T(h)1-type immune responses have been implicated in many autoimmune disorders, whereas T(h)2-type responses have been shown to inhibit autoimmune disease, the choice of adjuvant may be critical for the design of a safe and effective immunotherapy for Alzheimer's disease.
Figures

References
-
- Price DL, Sisodia SS. Cellular and molecular biology of Alzheimer’s disease and animal models. Annu Rev Med. 1994;45:435. - PubMed
-
- Verbeek MM, de Waal RM, Schipper JJ, Van Nostrand WE. Rapid degeneration of cultured human brain pericytes by amyloid beta protein. J Neurochem. 1997;68:1135. - PubMed
-
- Selkoe DJ. Alzheimer’s disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol Rev. 2001;81:741. - PubMed
-
- Helmuth L. New Alzheimer’s treatment that may ease the mind. Science. 2002;297:1260. - PubMed
-
- Schenk D, Barbour R, Dunn W, Gordon G, Grajeda H, Guido T, Hu K, Huang J, Johnson-Wood K, Khan K, Kholodenko D, Lee M, Liao Z, Lieberburg I, Motter R, Mutter L, Soriano F, Shopp G, Vasquez N, Vandevert C, Walker S, Wogulis M, Yednock T, Games D, Seubert P. Immunization with amyloid-beta attenuates Alzheimer-disease-like pathology in the PDAPP mouse [see Comments] Nature. 1999;400:173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

