Changes in rhinovirus protein 2C allow efficient replication in mouse cells
- PMID: 12663784
- PMCID: PMC152148
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.8.4773-4780.2003
Changes in rhinovirus protein 2C allow efficient replication in mouse cells
Abstract
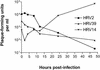
Rhinovirus type 16 was found to replicate in mouse L cells that express the viral receptor, human intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1). However, infection of these cells at a low multiplicity of infection leads to no discernible cytopathic effect, and low virus titers are produced. A variant virus, 16/L, was isolated after alternate passage of rhinovirus 16 between HeLa and ICAM-1 L cells. Infection of mouse cells with 16/L leads to higher virus titers, increased production of RNA, and total cytopathic effect. Three amino acid changes were identified in the P2 region of virus 16/L, and the adaptation phenotype mapped to two changes in protein 2C. The characterization of a rhinovirus host range mutant will facilitate the investigation of cellular proteins required for efficient viral growth and the development of a murine model for rhinovirus infection.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Amino acid changes in proteins 2B and 3A mediate rhinovirus type 39 growth in mouse cells.J Virol. 2005 May;79(9):5363-73. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.9.5363-5373.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15827151 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse respiratory epithelial cells support efficient replication of human rhinovirus.J Gen Virol. 2003 Oct;84(Pt 10):2829-2836. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.19109-0. J Gen Virol. 2003. PMID: 13679617
-
Interaction of picornavirus 2C polypeptide with the viral negative-strand RNA.J Gen Virol. 2001 Nov;82(Pt 11):2621-2627. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-82-11-2621. J Gen Virol. 2001. PMID: 11602773
-
Viral cell recognition and entry.Protein Sci. 1994 Oct;3(10):1712-25. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560031010. Protein Sci. 1994. PMID: 7849588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Replication of rhinoviruses.Arch Virol. 1976;51(3):169-89. doi: 10.1007/BF01318022. Arch Virol. 1976. PMID: 61746 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Involvement of a joker mutation in a polymerase-independent lethal mutagenesis escape mechanism.Virology. 2016 Jul;494:257-66. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2016.04.023. Epub 2016 Apr 29. Virology. 2016. PMID: 27136067 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse models of rhinovirus-induced disease and exacerbation of allergic airway inflammation.Nat Med. 2008 Feb;14(2):199-204. doi: 10.1038/nm1713. Epub 2008 Feb 3. Nat Med. 2008. PMID: 18246079 Free PMC article.
-
The minor receptor group of human rhinovirus (HRV) includes HRV23 and HRV25, but the presence of a lysine in the VP1 HI loop is not sufficient for receptor binding.J Virol. 2005 Jun;79(12):7389-95. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.12.7389-7395.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15919894 Free PMC article.
-
Human rhinovirus 1B exposure induces phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent airway inflammation in mice.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008 May 15;177(10):1111-21. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200708-1243OC. Epub 2008 Feb 14. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008. PMID: 18276942 Free PMC article.
-
Stimulator of interferon genes (STING) is an essential proviral host factor for human rhinovirus species A and C.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Nov 3;117(44):27598-27607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2014940117. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 33060297 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agirre, A., A. Barco, L. Carrasco, and J. Nieva. 2002. Viroporin-mediated membrane permeabilization. J. Biol. Chem. 277:40434-40441. - PubMed
-
- Aldabe, R., A. Barco, and L. Carrasco. 1996. Membrane permeabilization by poliovirus proteins 2B and 2BC. J. Biol. Chem. 271:23134-23137. - PubMed
-
- Aldabe, R., and L. Carrasco. 1995. Induction of membrane proliferation by poliovirus proteins 2C and 2BC. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 206:64-76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

