Murine coronavirus-induced hepatitis: JHM genetic background eliminates A59 spike-determined hepatotropism
- PMID: 12663803
- PMCID: PMC152168
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.8.4972-4978.2003
Murine coronavirus-induced hepatitis: JHM genetic background eliminates A59 spike-determined hepatotropism
Abstract
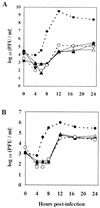
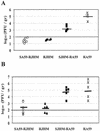
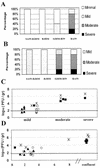
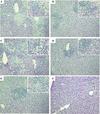
Recombinant murine coronaviruses, differing only in the spike gene and containing the strain A59 (moderately hepatotropic) and JHM (neurotropic) spike genes in the background of the JHM genome, were compared for the ability to replicate in the liver and induce hepatitis in weanling C57BL/6 mice. Interestingly, expression of the A59 spike glycoprotein within the background of the neurotropic JHM strain does not reproduce the A59 hepatotropic phenotype. Thus, the JHM genetic background plays a dominant role over the spike in the determination of hepatotropism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Murine coronavirus spike protein determines the ability of the virus to replicate in the liver and cause hepatitis.J Virol. 2001 Mar;75(5):2452-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.5.2452-2457.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11160748 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted recombination within the spike gene of murine coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus-A59: Q159 is a determinant of hepatotropism.J Virol. 1998 Dec;72(12):9628-36. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.12.9628-9636.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9811696 Free PMC article.
-
Murine coronavirus evolution in vivo: functional compensation of a detrimental amino acid substitution in the receptor binding domain of the spike glycoprotein.J Virol. 2005 Jun;79(12):7629-40. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.12.7629-7640.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15919915 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor specificity and receptor-induced conformational changes in mouse hepatitis virus spike glycoprotein.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2001;494:173-81. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-1325-4_29. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2001. PMID: 11774465 Review. No abstract available.
-
Murine coronavirus neuropathogenesis: determinants of virulence.J Neurovirol. 2010 Nov;16(6):427-34. doi: 10.3109/13550284.2010.529238. Epub 2010 Nov 12. J Neurovirol. 2010. PMID: 21073281 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of hemagglutinin esterase protein from recombinant mouse hepatitis virus enhances neurovirulence.J Virol. 2005 Dec;79(24):15064-73. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.24.15064-15073.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16306577 Free PMC article.
-
Homologous 2',5'-phosphodiesterases from disparate RNA viruses antagonize antiviral innate immunity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Aug 6;110(32):13114-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1306917110. Epub 2013 Jul 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23878220 Free PMC article.
-
Differential induction of proinflammatory cytokines in primary mouse astrocytes and microglia by coronavirus infection.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006;581:407-10. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-33012-9_73. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006. PMID: 17037569 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
MDA5 Is Critical to Host Defense during Infection with Murine Coronavirus.J Virol. 2015 Dec;89(24):12330-40. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01470-15. Epub 2015 Sep 30. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26423942 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the replicase gene of murine coronavirus JHM strain in hepatitis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006;581:415-20. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-33012-9_75. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006. PMID: 17037571 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Batts, K. P., and J. Ludwig. 1995. Chronic hepatitis: an update on terminology and reporting. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 19:1409-1417. - PubMed
-
- Ding, J. W., Q. Ning, M. F. Liu, A. Lai, J. Leibowitz, K. M. Peltekian, E. H. Cole, L. S. Fung, C. Holloway, P. A. Marsden, H. Yeger, M. J. Phillips, and G. A. Levy. 1997. Fulminant hepatic failure in murine hepatitis virus strain 3 infection: tissue-specific expression of a novel fgl2 prothrombinase. J. Virol. 71:9223-9230. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

