Mucosal CD8alpha+ DC, with a plasmacytoid phenotype, induce differentiation and support function of T cells with regulatory properties
- PMID: 12667210
- PMCID: PMC1782923
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2003.01606.x
Mucosal CD8alpha+ DC, with a plasmacytoid phenotype, induce differentiation and support function of T cells with regulatory properties
Abstract
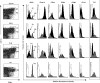
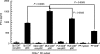
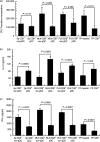
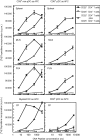
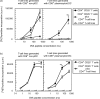
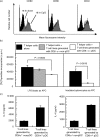
Repetitive stimulation of naïve T cells by immature splenic dendritic cells (DC) can result in the differentiation of T-cell lines with regulatory properties. In the present study we identified a population of DC in the mucosae that exhibit the plasmacytoid phenotype, secrete interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) following stimulation with oligodeoxynucleotides containing certain cytosine-phosphate-guanosine (CpG) motifs and can differentiate naïve T cells into cells that exhibit regulatory properties. Although these DC appear to be present in both spleen and mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN), only CpG-matured DC from the MLN (but not the spleen) were able to differentiate naïve T cells into T regulatory 1-like cells with regulatory properties. The activity of these DC failed to sustain robust T-cell proliferation and thereby enhanced the suppressive efficacy of CD4+ CD25+ T regulatory cells. These DC are the major CD8alpha+ DC population in the Peyer's patches (PP). Given their significant presence in mucosal tissue, we propose that these DC may provide a mechanistic basis for the homeostatic regulation in the gut by eliciting regulatory cell suppressor function and poorly supporting T helper cell proliferation at a site of high antigenic stimulation like the intestine.
Figures

References
-
- Shortman K, Caux C. Dendritic cell development: multiple pathways to nature's adjuvants. Stem Cells. 1997;15:409–19. - PubMed
-
- Vremec D, Shortman K. Dendritic cell subtypes in mouse lymphoid organs: cross-correlation of surface markers, changes with incubation, and differences among thymus, spleen, and lymph nodes. J Immunol. 1997;159:565–73. - PubMed
-
- Kronin V, Winkel K, Suss G, Kelso A, Heath W, Kirberg J, von Boehmer H, Shortman K. A subclass of dendritic cells regulates the response of naive CD8 T cells by limiting their IL-2 production. J Immunol. 1996;157:3819–27. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

