Suppression of sucrose synthase gene expression represses cotton fiber cell initiation, elongation, and seed development
- PMID: 12671090
- PMCID: PMC152341
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.010108
Suppression of sucrose synthase gene expression represses cotton fiber cell initiation, elongation, and seed development
Abstract
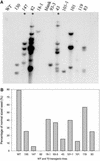
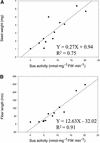
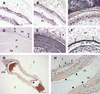
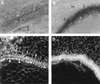
Cotton is the most important textile crop as a result of its long cellulose-enriched mature fibers. These single-celled hairs initiate at anthesis from the ovule epidermis. To date, genes proven to be critical for fiber development have not been identified. Here, we examined the role of the sucrose synthase gene (Sus) in cotton fiber and seed by transforming cotton with Sus suppression constructs. We focused our analysis on 0 to 3 days after anthesis (DAA) for early fiber development and 25 DAA, when the fiber and seed are maximal in size. Suppression of Sus activity by 70% or more in the ovule epidermis led to a fiberless phenotype. The fiber initials in those ovules were fewer and shrunken or collapsed. The level of Sus suppression correlated strongly with the degree of inhibition of fiber initiation and elongation, probably as a result of the reduction of hexoses. By 25 DAA, a portion of the seeds in the fruit showed Sus suppression only in the seed coat fibers and transfer cells but not in the endosperm and embryo. These transgenic seeds were identical to wild-type seeds except for much reduced fiber growth. However, the remaining seeds in the fruit showed Sus suppression both in the seed coat and in the endosperm and embryo. These seeds were shrunken with loss of the transfer cells and were <5% of wild-type seed weight. These results demonstrate that Sus plays a rate-limiting role in the initiation and elongation of the single-celled fibers. These analyses also show that suppression of Sus only in the maternal seed tissue represses fiber development without affecting embryo development and seed size. Additional suppression in the endosperm and embryo inhibits their own development, which blocks the formation of adjacent seed coat transfer cells and arrests seed development entirely.
Figures





References
-
- Basra, A., and Malik, C.P. (1984). Development of the cotton fiber. Int. Rev. Cytol. 89, 65–113.
-
- Buchala, A.J. (1999). Noncellulosic carbohydrates in cotton fibers. In Cotton Fibers: Developmental Biology, Quality Improvement and Textile Processing, A.S. Basra, ed (New York: Food Products Press), pp. 113–136.
-
- Chengappa, S., Guilleroux, M., Phillips, W., and Shields, R. (1999). Transgenic tomato plants with decreased sucrose synthase are unaltered in starch and sugar accumulation in the fruit. Plant Mol. Biol. 40, 213–221. - PubMed
-
- Chourey, P.S., Chen, Y.C., and Miller, M.E. (1991). Early cell degeneration in developing endosperm is unique to the Shrunken mutation in maize. Maydica 36, 141–146.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

