Is there a cloud in the silver lining for imatinib?
- PMID: 12671692
- PMCID: PMC2376361
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600828
Is there a cloud in the silver lining for imatinib?
Abstract
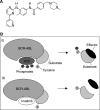
Imatinib mesylate (Gleevec) or Glivec), a small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukaemia, has been said to herald the dawn of a new era of rationally designed, molecularly targeted oncotherapy. Lurking on the same new horizon, however, is the age-old spectre of drug resistance. This review sets the intoxicating clinical perspective against the more sobering laboratory evidence of such divergent mechanisms of imatinib resistance as gene amplification and stem cell quiescence. Polychemotherapy has already been considered to combat resistance, but a more innovative, as yet unformulated, approach may be advocated.
Figures
References
-
- Barthe C, Cony-Makhoul P, Melo J, Mahon J (2001) Roots of clinical resistance to STI-571 cancer therapy. Science 293: 2163 - PubMed
-
- Branford S, Rudzki Z, Walsh S, Grigg A, Arthur C, Taylor K, Herrmann R, Lynch K, Hughes T (2002) High frequency of point mutations clustered within the adenosine triphosphate-binding region of BCR/ABL in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia or Ph-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia who develop imatinib (STI571) resistance. Blood 99: 3472–3475 - PubMed
-
- Brinkmann U, Roots I, Eichelbaum M (2001) Pharmacogenetics of the human drug-transporter gene MDR1: impact of polymorphisms on pharmacotherapy. Drug Discov Today 6: 835–839 - PubMed
-
- Deininger M, Leiblein S, Keohler T, Guenther R, Kovacs I, Ben-Am M, Al-Ali H, Reiner K, Niederwieser D (2001) In vivo resistance to Glivec is not consistantly associated with resistance in vitro but may be related to increased MDR-1 expression. Blood 98: 176b
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

