Impact of epoetin beta on quality of life in patients with malignant disease
- PMID: 12671693
- PMCID: PMC2376376
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600801
Impact of epoetin beta on quality of life in patients with malignant disease
Abstract
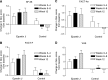
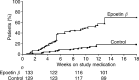
This open-label, prospective study was conducted to compare the impact of epoetin beta vs standard care on quality of life (QoL) in anaemic patients with lymphoid or solid tumour malignancies. A total of 262 anaemic patients (haemoglobin [Hb]<or=11 g dl(-1)) were randomised to a 12-week treatment with s.c. epoetin beta (initial dose 150 IU kg(-1) three times weekly) or standard care. Transfusions were recommended for both groups at an Hb threshold of 8.5 g dl(-1). The primary efficacy variables were improvement in QoL as measured using the Short-Form-36 physical component summary (SF-36 PCS) score and the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy fatigue and anaemia subscales (FACT-F and FACT-An). A visual analogue scale (VAS) was also used as a global QoL measure. Clinical response was defined as a >or=2 g dl(-1) increase in Hb level without need of transfusion after the initial 4 weeks of treatment. Baseline to final visit changes in SF-36 PCS, FACT-F and VAS scores were significantly greater with epoetin beta than with standard care (P<0.05); changes in FACT-An subscale score tended to be greater with epoetin beta (P=0.076). Epoetin beta significantly increased Hb concentrations relative to standard care (responders: 47% vs 13%; P<0.001). Levels of endogenous erythropoietin <50 mIU ml(-1) were significantly predictive of response (OR 2.496, 95% CI: 1.21-5.13). Epoetin beta therapy significantly improves QoL compared with standard care in anaemic patients with solid tumours and lymphoid malignancies.
Figures


References
-
- Barosi G, Cazzola M, De Vincentiis A, Grossi A, Tura S (1994) Guidelines for the use of recombinant human erythropoietin. Haematologica 79: 526–533 - PubMed
-
- Beguin Y, Yerna M, Loo M, Weber M, Fillet G (1992) Erythropoiesis in multiple myeloma: defective red cell production due to inappropriate erythropoietin production. Br J Haematol 82: 648–653 - PubMed
-
- Caro JJ, Salas M, Ward A, Goss G (2001) Anemia as an independent prognostic factor for survival in patients with cancer. Cancer 91: 2214–2221 - PubMed
-
- Cascinu S, Fedeli A, Del Ferro E, Luzi Fedeli S, Catalano G (1994) Recombinant human erythropoietin treatment in cisplatin-associated anemia: a randomized, double-blind trial with placebo. J Clin Oncol 12: 1058–1062 - PubMed
-
- Case DC, Bukowski RM, Carey RW, Fishkin EH, Henry DH, Jacobson RJ, Jones SE, Keller AM, Kugler JW, Nichols CR, Salmon SE, Silver RT, Storniolo AM, Wampler GL, Dooley CM, Larholt KM, Nelson RA, Abels RI (1993) Recombinant human erythropoietin therapy for anemic cancer patients on combination chemotherapy. J Natl Cancer Inst 85: 801–806 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

