Prognostic importance of survivin in breast cancer
- PMID: 12671708
- PMCID: PMC2376388
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600776
Prognostic importance of survivin in breast cancer
Abstract
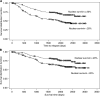
Survivin is a member of the inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) family, and is also involved in the regulation of cell division. Survivin is widely expressed in foetal tissues and in human cancers, but generally not in normal adult tissue. This study examined the expression of surviving protein in a series of 293 cases of invasive primary breast carcinoma. Survivin immunoreactivity was assessed using two different polyclonal antibodies, and evaluated semiquantitatively according to the percentage of cells demonstrating distinct nuclear and/or diffuse cytoplasmic staining. Overall, 60% of tumours were positive for survivin: 31% demonstrated nuclear staining only, 13% cytoplasmic only, and 16% of tumour cells demonstrated both nuclear and cytoplasmic staining. Statistical analysis revealed that survivin expression was independent of patient's age, tumour size, histological grade, nodal status, and oestrogen receptor status. In multivariate analysis, nuclear survivin expression was a significant independent prognostic indicator of favourable outcome both in relapse-free and overall survival (P<0.001 and P=0.01, respectively). In conclusion, our results show that survivin is frequently overexpressed in primary breast cancer. Nuclear expression is most common and is an independent prognostic indicator of good prognosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression of survivin and clinical correlation in patients with breast cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2006 Jul;60(6):289-92. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2006.06.008. Epub 2006 Jun 23. Biomed Pharmacother. 2006. PMID: 16876381
-
Nuclear and cytoplasmic cellular distribution of survivin as survival predictor in resected non-small-cell lung cancer.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2008 May;34(5):593-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2007.06.002. Epub 2007 Aug 10. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2008. PMID: 17693049
-
A new subtype-specific monoclonal antibody for IAP-survivin identifies high-risk patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and improves the prognostic value of bcl-2.Int J Oncol. 2008 Jan;32(1):59-68. Int J Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18097543
-
Survivin beyond physiology: orchestration of multistep carcinogenesis and therapeutic potentials.Cancer Lett. 2014 Jun 1;347(2):175-82. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.02.014. Epub 2014 Feb 19. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 24560928 Review.
-
Overview of role of survivin in cancer: expression, regulation, functions, and its potential as a therapeutic target.J Drug Target. 2024 Dec;32(3):223-240. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2024.2309563. Epub 2024 Feb 1. J Drug Target. 2024. PMID: 38252514 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of synergistic anti-cancer effects of docosahexaenoic acid and curcumin on DMBA-induced mammary tumorigenesis in mice.BMC Cancer. 2013 Sep 13;13:418. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-418. BMC Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24034496 Free PMC article.
-
The abnormal expression of chromosomal region maintenance 1 (CRM1)-survivin axis in ovarian cancer and its related mechanisms regulating proliferation and apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells.Bioengineered. 2022 Jan;13(1):624-633. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2012416. Bioengineered. 2022. Retraction in: Bioengineered. 2024 Dec;15(1):2299572. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2024.2299572. PMID: 34898375 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Survivin withdrawal by nuclear export failure as a physiological switch to commit cells to apoptosis.Cell Death Dis. 2010 Jul 22;1(7):e57. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2010.34. Cell Death Dis. 2010. PMID: 21364662 Free PMC article.
-
Tumour cell survival mechanisms in lethal metastatic prostate cancer differ between bone and soft tissue metastases.J Pathol. 2013 Jul;230(3):291-7. doi: 10.1002/path.4180. J Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23420560 Free PMC article.
-
The pattern of prognostic and risk indicators among women with breast cancer undergoing modified radical mastectomy in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania.Infect Agent Cancer. 2016 Jun 30;11:28. doi: 10.1186/s13027-016-0075-8. eCollection 2016. Infect Agent Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27366204 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adida C, Haioun C, Gaulard P, Lepage E, Morel P, Briere J, Dombret H, Reyes F, Diebold J, Gisselbrecht C, Salles G, Altieri DC, Molina TJ (2000a) Prognostic significance of survivin expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood 96: 1921–1925 - PubMed
-
- Adida C, Recher C, Raffoux E, Daniel MT, Taksin AL, Rousselot P, Sigaux F, Degos L, Altieri DC, Dombret H (2000b) Expression and prognostic significance of survivin in de novo acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol 111: 196–203 - PubMed
-
- Ambrosini G, Adida C, Altieri DC (1997) A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nat Med 3: 917–921 - PubMed
-
- Ambrosini G, Adida C, Sirugo G, Altieri DC (1998) Induction of apoptosis and inhibition of cell proliferation by survivin gene targeting. J Biol Chem 273: 11177–11182 - PubMed
-
- Deveraux QL, Reed JC (1999) IAP family proteins – suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev 13: 239–252 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

