For the insect pathogen Photorhabdus luminescens, which end of a nematode is out?
- PMID: 12676661
- PMCID: PMC154793
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.69.4.1890-1897.2003
For the insect pathogen Photorhabdus luminescens, which end of a nematode is out?
Abstract
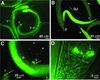
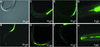
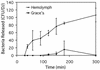
The nematode Heterorhabditis bacteriophora is the vector for transmitting the entomopathogenic bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens between insect larvae. The dauer juvenile (DJ) stage nematode selectively retains P. luminescens in its intestine until it releases the bacteria into the hemocoel of an insect host. We report the results of studying the transmission of the bacteria by its nematode vector. Cells of P. luminescens labeled with green fluorescent protein preferentially colonized a region of the DJ intestine immediately behind the basal bulb, extending for various distances toward the anus. Incubation of DJ nematodes in vitro in insect hemolymph induced regurgitation of the bacteria. Following a 30-min lag, the bacteria migrated in a gradual and staggered movement toward and ultimately exited the mouth. This regurgitation reaction was induced by a low-molecular-weight, heat- and protease-stable, anionic component present in arthropod hemolymph and in supernatants from insect cell cultures. Nematodes anesthetized with levamisole or treated with the antihelmenthic agent ivermectin did not release their bacteria into hemolymph. The ability to visualize P. luminescens in the DJ nematode intestine provides the first clues to the mechanism of release of the bacteria during infection of insect larvae. This and the partial characterization of a component of hemolymph triggering release of the bacteria render this fascinating example of both a mutualistic symbiosis and disease transmission amenable to future genetic and molecular study.
Figures

References
-
- Akhurst, R. J., R. G. Mourant, L. Baud, and N. E. Boemare. 1996. Phenotypic and DNA relatedness study between nematode-symbiotic and clinical strains of the genus Photorhabditis (Enterobacteriaceae). Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 43:249-255. - PubMed
-
- Bartolome, B., Y. Jubete, E. Martinez, and F. de la Cruz. 1991. Construction and properties of a family of pACYC 184-derived cloning vectors compatible with pBR322 and its derivatives. Gene 102:75-78. - PubMed
-
- Bedding, R. A., and A. S. Molyneux. 1982. Penetration of insect cuticle by infective juveniles of Heterorhabditis spp. (Heterorhabditidae: Nematoda). Nematologica 28:354-359.
-
- Blaxter, M. L., P. De Ley, J. R. Garey, L. X. Liu, P. Scheldeman, A. Vierstraete, J. R. Vanfleteren, L. Y. Mackey, M. Dorris, L. M. Frisse, J. T. Vida, and W. K. Thomas. 1998. A molecular evolutionary framework for the phylum Nematoda. Nature 392:71-75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

