Identification of equine cecal bacteria producing amines in an in vitro model of carbohydrate overload
- PMID: 12676687
- PMCID: PMC154823
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.69.4.2087-2093.2003
Identification of equine cecal bacteria producing amines in an in vitro model of carbohydrate overload
Abstract
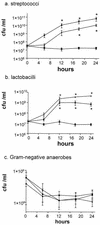
Acute laminitis has been associated with the overgrowth of gram-positive bacteria within the equine hindgut, causing the release of factor(s) leading to ischemia-reperfusion of the digits. The products of fermentation which trigger acute laminitis are, as yet, unknown; however, vasoactive amines are possible candidates. The objectives of this study were to use an in vitro model of carbohydrate overload to study the change in populations of cecal streptococci and lactobacilli and to establish whether certain species of these bacteria were capable of producing vasoactive amines from amino acids. Cecal contents from 10 horses were divided into aliquots and incubated anaerobically with either corn starch or inulin (fructan; both at 1 g/100 ml). Samples were taken at 6-h intervals over a 24-h period for enumeration of streptococci, lactobacilli, and gram-negative anaerobes by a dilution method onto standard selective growth media. The effects of the antibiotic virginiamycin (1 mg/100 ml) and calcium hydrogen phosphate (CaHPO(4); 0.3 g/100 ml) were also examined. Fermentation of excess carbohydrate was associated with increases in numbers of streptococci and lactobacilli (2- to 3.5-log unit increases; inhibited by virginiamycin) but numbers of gram-negative anaerobes were not significantly affected. A screening agar technique followed by 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis enabled the identification of 26 different bacterial strains capable of producing one or more vasoactive amines. These included members of the species Streptococcus bovis and five different Lactobacillus spp. These data suggest that certain bacteria, whose overgrowth is associated with carbohydrate fermentation, are capable of producing vasoactive amines which may play a role in the pathogenesis of acute laminitis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Production of amines in equine cecal contents in an in vitro model of carbohydrate overload.J Anim Sci. 2002 Oct;80(10):2656-62. doi: 10.2527/2002.80102656x. J Anim Sci. 2002. PMID: 12413088
-
Illumina sequencing of the V4 hypervariable region 16S rRNA gene reveals extensive changes in bacterial communities in the cecum following carbohydrate oral infusion and development of early-stage acute laminitis in the horse.Vet Microbiol. 2014 Jan 31;168(2-4):436-41. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2013.11.017. Epub 2013 Nov 26. Vet Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24355533
-
Dietary fructan carbohydrate increases amine production in the equine large intestine: implications for pasture-associated laminitis.J Anim Sci. 2007 Nov;85(11):2949-58. doi: 10.2527/jas.2006-600. Epub 2007 Jun 25. J Anim Sci. 2007. PMID: 17591708
-
Microbial events in the hindgut during carbohydrate-induced equine laminitis.Vet Clin North Am Equine Pract. 2010 Apr;26(1):79-94. doi: 10.1016/j.cveq.2010.01.007. Vet Clin North Am Equine Pract. 2010. PMID: 20381737 Review.
-
Carbohydrate alimentary overload laminitis.Vet Clin North Am Equine Pract. 2010 Apr;26(1):65-78. doi: 10.1016/j.cveq.2010.01.006. Vet Clin North Am Equine Pract. 2010. PMID: 20381736 Review.
Cited by
-
Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium diversity in horse feces, revealed by PCR-DGGE.Curr Microbiol. 2009 Dec;59(6):651-5. doi: 10.1007/s00284-009-9498-4. Curr Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19730939
-
Effects of Disodium Fumarate on In Vitro Rumen Fermentation, The Production of Lipopolysaccharide and Biogenic Amines, and The Rumen Bacterial Community.Curr Microbiol. 2017 Nov;74(11):1337-1342. doi: 10.1007/s00284-017-1322-y. Epub 2017 Jul 31. Curr Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28761980
-
In vitro assessment of probiotic potential of selected bacteria isolated from pig faeces with potential application of odour reduction.Int J Vet Sci Med. 2021 Jul 2;9(1):22-30. doi: 10.1080/23144599.2021.1936962. eCollection 2021. Int J Vet Sci Med. 2021. PMID: 34277842 Free PMC article.
-
Stability of Gastric Fluid and Fecal Microbial Populations in Healthy Horses under Pasture and Stable Conditions.Animals (Basel). 2024 Oct 16;14(20):2979. doi: 10.3390/ani14202979. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457909 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors for acute abdominal pain (colic) in the adult horse: A scoping review of risk factors, and a systematic review of the effect of management-related changes.PLoS One. 2019 Jul 11;14(7):e0219307. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0219307. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31295284 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al Jassim, R. A. M., and J. B. Rowe. 1999. Better understanding of acidosis and its control. Rec. Adv. Anim. Nutr. Aust. 12:91-97.
-
- Allison, M. J., I. M. Robinson, R. W. Dougherty, and J. A. Bucklin. 1975. Grain overload in cattle and sheep: changes in microbial populations in the caecum and rumen. Am. J. Vet. Res. 36:181-185. - PubMed
-
- Bailey, S. R., and J. Elliott. 1998. Plasma 5-hydroxytryptamine constricts equine digital blood vessels in vitro: implications for the pathogenesis of acute laminitis. Equine Vet. J. 30:124-130. - PubMed
-
- Bailey, S. R., A. N. Rycroft, and J. Elliott. 2002. Production of amines in an in vitro model of carbohydrate overload. J. Anim. Sci. 80:2656-2662. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

