Selection and identification of a Listeria monocytogenes target strain for pulsed electric field process optimization
- PMID: 12676704
- PMCID: PMC154796
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.69.4.2223-2229.2003
Selection and identification of a Listeria monocytogenes target strain for pulsed electric field process optimization
Abstract
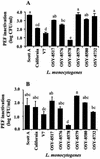
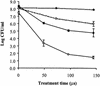
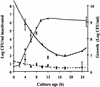
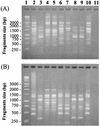
Nine Listeria monocytogenes strains were treated individually with a continuous pulsed electric field (PEF) apparatus, and their sensitivities to the treatment were compared at 25 kV/cm. When cell suspensions of these strains in 0.1% NaCl (pH 7.0) were treated at 23 degrees C for 144 micro s, inactivation ranged from 0.7 to 3.7 log(10) CFU/ml. Inactivation by 72- micro s PEF treatments at 37 degrees C ranged from 0.3 to 2.5 log(10) CFU/ml. L. monocytogenes OSY-8578 was substantially more resistant than other strains when cells were PEF treated in 0.1% NaCl, whereas Scott A was one of the most sensitive strains. The superiority of OSY-8578's resistance to that of Scott A was confirmed in 50% diluted acid whey (pH 4.2). Changes in sensitivity to PEF during phases of growth were minimal in OSY-8578 and substantial in Scott A. Use of L. monocytogenes OSY-8578, therefore, is recommended in studies to optimize PEF processes that target L. monocytogenes. The nine L. monocytogenes strains were genotyped with pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) and arbitrarily primed PCR (AP-PCR) techniques. These strains were better differentiated with PFGE than with AP-PCR. The target strain (OSY-8578) was characterized by both molecular typing techniques, but resistance to PEF, in general, was not associated with a particular genotype group.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pulsed electric field alters molecular chaperone expression and sensitizes Listeria monocytogenes to heat.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004 Apr;70(4):2289-95. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.4.2289-2295.2004. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15066824 Free PMC article.
-
Screening for Listeria monocytogenes surrogate strains applicable to food processing by ultrahigh pressure and pulsed electric field.J Food Prot. 2011 Oct;74(10):1655-61. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-11-099. J Food Prot. 2011. PMID: 22004812
-
Inactivation kinetics of pulsed electric field-resistant strains of Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus in media of different pH.Food Microbiol. 2010 Jun;27(4):550-8. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2010.01.002. Epub 2010 Jan 25. Food Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20417406
-
Inactivation of Escherichia coli O1 57:H7, Listeria monocytogenes, and Lactobacillus leichmannii by combinations of ozone and pulsed electric field.J Food Prot. 2001 Jun;64(6):777-82. doi: 10.4315/0362-028x-64.6.777. J Food Prot. 2001. PMID: 11403125
-
Listeria monocytogenes: Strain Heterogeneity, Methods, and Challenges of Subtyping.J Food Sci. 2015 Dec;80(12):M2868-78. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.13133. Epub 2015 Nov 20. J Food Sci. 2015. PMID: 26588067 Review.
Cited by
-
Genes of Escherichia coli O157:H7 that are involved in high-pressure resistance.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006 Apr;72(4):2661-71. doi: 10.1128/AEM.72.4.2661-2671.2006. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16597971 Free PMC article.
-
An Exploration of Listeria monocytogenes, Its Influence on the UK Food Industry and Future Public Health Strategies.Foods. 2022 May 17;11(10):1456. doi: 10.3390/foods11101456. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35627026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulsed electric field alters molecular chaperone expression and sensitizes Listeria monocytogenes to heat.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004 Apr;70(4):2289-95. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.4.2289-2295.2004. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15066824 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance of Listeria monocytogenes to Stress Conditions Encountered in Food and Food Processing Environments.Front Microbiol. 2018 Nov 13;9:2700. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02700. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30555426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phylogenetic and genetic characterization of Acidithiobacillus strains isolated from different environments.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014 Dec;30(12):3197-209. doi: 10.1007/s11274-014-1747-4. Epub 2014 Sep 25. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25252934
References
-
- Aronsson, K., M. Lindgren, B. R. Johansson, and U. Ronner. 2001. Inactivation of microorganisms using pulsed electric fields: the influence of process parameters on Escherichia coli, Listeria innocua, Leuconostoc mesenteroides and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2:41-54.
-
- Bender, J. B., C. W. Hedberg, D. J. Boxrud, J. M. Besser, J. H. Wicklund, K. E. Smith, and M. T. Osterholm. 2001. Use of molecular subtyping in surveillance for Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium. N. Engl. J. Med. 344:189-195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

