Closing the loop: the PmrA/PmrB two-component system negatively controls expression of its posttranscriptional activator PmrD
- PMID: 12676988
- PMCID: PMC153620
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0836837100
Closing the loop: the PmrA/PmrB two-component system negatively controls expression of its posttranscriptional activator PmrD
Abstract
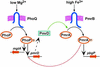
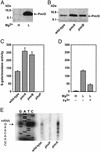
A fundamental question in biology is how an organism integrates multiple signals to mediate an appropriate cellular response. The PmrAPmrB two-component system of Salmonella enterica can be activated independently by Fe(3+), which is sensed by the PmrB protein, and in low Mg(2+), which is sensed by the PhoQ protein. The low-Mg(2+) activation requires pmrD, a PhoPPhoQ-activated gene that activates the response regulator PmrA at a posttranscriptional level. We now report that pmrD expression is negatively regulated by the PmrAPmrB system. Conditions that activate the PmrA protein independently of pmrD, such as exposure to Fe(3+), resulted in lower levels of pmrD transcription. The PmrA protein footprinted the pmrD promoter upstream of the PhoP-binding site but did not interfere with binding of the PhoP protein. Mutation of the PmrA-binding site in the pmrD promoter abolished PmrA-mediated repression. Negative regulation of the PhoPPhoQ-activated pmrD gene by the PmrAPmrB system closes a regulatory circuit designed to maintain proper cellular levels of activated PmrA protein and constitutes a singular example of a multicomponent feedback loop.
Figures

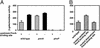
Similar articles
-
A small protein that mediates the activation of a two-component system by another two-component system.EMBO J. 2000 Apr 17;19(8):1861-72. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.8.1861. EMBO J. 2000. PMID: 10775270 Free PMC article.
-
Connecting two-component regulatory systems by a protein that protects a response regulator from dephosphorylation by its cognate sensor.Genes Dev. 2004 Sep 15;18(18):2302-13. doi: 10.1101/gad.1230804. Genes Dev. 2004. PMID: 15371344 Free PMC article.
-
Ancestral genes can control the ability of horizontally acquired loci to confer new traits.PLoS Genet. 2011 Jul;7(7):e1002184. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002184. Epub 2011 Jul 21. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 21811415 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation of the 4-amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinose biosynthetic genes in Yersinia pestis.J Biol Chem. 2005 Apr 15;280(15):14765-72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413900200. Epub 2005 Feb 14. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15710615
-
The biology of the PmrA/PmrB two-component system: the major regulator of lipopolysaccharide modifications.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2013;67:83-112. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-092412-155751. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23799815 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Signal transduction cascade between EvgA/EvgS and PhoP/PhoQ two-component systems of Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2004 May;186(10):3006-14. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.10.3006-3014.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15126461 Free PMC article.
-
The PmrA-regulated pmrC gene mediates phosphoethanolamine modification of lipid A and polymyxin resistance in Salmonella enterica.J Bacteriol. 2004 Jul;186(13):4124-33. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.13.4124-4133.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15205413 Free PMC article.
-
PhoP-Mediated Repression of the SPI1 Type 3 Secretion System in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium.J Bacteriol. 2019 Jul 24;201(16):e00264-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00264-19. Print 2019 Aug 15. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 31182495 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling by two-component system noncognate partners promotes intrinsic tolerance to polymyxin B in uropathogenic Escherichia coli.Sci Signal. 2017 Jan 10;10(461):eaag1775. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aag1775. Sci Signal. 2017. PMID: 28074004 Free PMC article.
-
Conflicting roles for a cell surface modification in Salmonella.Mol Microbiol. 2013 Jun;88(5):970-83. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12236. Epub 2013 May 5. Mol Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23646936 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

