Immunotolerance of liver allotransplantation induced by intrathymic inoculation of donor soluble liver specific antigen
- PMID: 12679927
- PMCID: PMC4611445
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i4.759
Immunotolerance of liver allotransplantation induced by intrathymic inoculation of donor soluble liver specific antigen
Abstract
Aim: To study the effects of liver specific antigen (LSA) on the immunoreaction of liver allotransplantation and its significance.
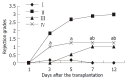
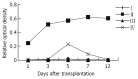
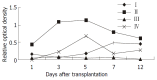
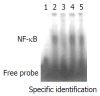
Methods: Orthotopic liver transplantation was used in this study. Group I: syngeneic control (Wistar-to-Wistar); Group II: acute rejection (SD-to-Wistar). Group III: acute rejection treated by intramuscular injection of cyclosporine A (CsA) (SD-to-Wistar+CsA). Group IV: Intrathymic inoculation of SD rat LSA one week before transplantation (LSA+SD-to-Wistar). The common situation and survival time, rejection grades, NF-kappaB activity of splenocytes and intragraft cytokine gene expression were observed to analyze the acute rejection severity and immune state of animals.
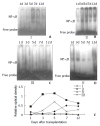
Results: The common situation of Wistar-to-Wistar group was very good after the transplantation and no signs of rejection were found. Recipients of SD-to-Wistar group lost body weight progressively. All died within 9 to 13 days after transplantation with the median survival time of 10.7+/-0.51 days. It was an optimal control for acute rejection. The common situation of SD-to-Wistar+CsA group was bad during CsA medication but only with mild rejection. As for LSA+SD-to-Wistar group, 5 of 6 recipients survived for a long time and common situation was remarkably better than that of SD-to-Wistar group and SD-to-Wistar+CsA group. Its rejection grades were significantly lower than that of SD-to-Wistar group (P=0.026). Furthermore, no significant discrepancies of rejection were found between SD-to-Wistar group and LSA+SD-to-Wistar group at day7 and day12 (P=0.067). NF-kappaB activity, IFN-gamma and IL-2mRNA expression were significantly inhibited in LSA+SD-to-Wistar group compared with that of SD-to-Wistar group (P<0.05).
Conclusion: LSA is an important transplantation antigen which involves in the immunorejection of liver transplantation directly. We reported for the first time that intrathymic inoculation of LSA can induce immnotolerance of liver allotransplantation and grafts can survive for a long time thereby, thus leading to a novel way to liver transplantation immunotolerance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intrathymic inoculation of donor liver specific antigen alleviates rejection of liver allotransplantation.J Zhejiang Univ Sci. 2003 Jul-Aug;4(4):485-90. doi: 10.1631/jzus.2003.0485. J Zhejiang Univ Sci. 2003. PMID: 12861628
-
Intrathymic inoculation of liver specific antigen alleviates liver transplant rejection.Chin Med Sci J. 2004 Mar;19(1):38-43. Chin Med Sci J. 2004. PMID: 15104223
-
Infusion of nonmyeloablative bone marrow alleviates acute rejection reaction in liver allotransplantation.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2005 Dec;6(12):1188-94. doi: 10.1631/jzus.2005.B1188. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2005. PMID: 16358377 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on preventing allograft from acute rejection following rat orthotopic liver transplantation.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 May;9(5):1067-71. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i5.1067. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12717858 Free PMC article.
-
Immunosuppression after liver transplantation.J Hepatol. 1996 Apr;24(4):503-5. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(96)80173-5. J Hepatol. 1996. PMID: 8738739 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Influence of liver nonparenchymal cell infusion combined with cyclosporin A on rejection of rat small bowel transplantation.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Dec;9(12):2859-62. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i12.2859. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 14669353 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of NF-kappaB and human telomerase reverse transcriptase in gastric cancer and precancerous lesions.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Jan 15;10(2):177-81. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i2.177. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 14716817 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological Tolerance in Liver Transplant Recipients: Putative Involvement of Neuroendocrine-Immune Interactions.Cells. 2022 Jul 29;11(15):2327. doi: 10.3390/cells11152327. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35954171 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Donaldson P, Underhill J, Doherty D, Hayllar K, Calne R, Tan KC, O'Grady J, Wight D, Portmann B, Williams R. Influence of human leukocyte antigen matching on liver allograft survival and rejection: "the dualistic effect". Hepatology. 1993;17:1008–1015. - PubMed
-
- Doran TJ, Derley L, Chapman J, McCaughan G, Painter D, Dorney S, Sheil AG. Severity of liver transplantation rejection is associated with recipient HLA type. Transplant Proc. 1992;24:192–193. - PubMed
-
- Yan YH, Liu GZ. Transplantation antigens. In: YiZhi MianYi Xue., editor. Wuhan: Hubei Science and Technology Press; 1998. pp. 45–47.
-
- Lohse AW, Dienes HP, Meyer zum Büschenfelde KH. Suppression of murine experimental autoimmune hepatitis by T-cell vaccination or immunosuppression. Hepatology. 1998;27:1536–1543. - PubMed
-
- Kamada N, Calne RY. A surgical experience with five hundred thirty liver transplants in the rat. Surgery. 1983;93:64–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

