Cellular remodeling in heart failure disrupts K(ATP) channel-dependent stress tolerance
- PMID: 12682006
- PMCID: PMC154482
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg192
Cellular remodeling in heart failure disrupts K(ATP) channel-dependent stress tolerance
Abstract
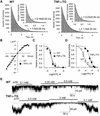
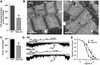
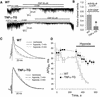
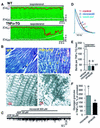
ATP-sensitive potassium (K(ATP)) channels are required for maintenance of homeostasis during the metabolically demanding adaptive response to stress. However, in disease, the effect of cellular remodeling on K(ATP) channel behavior and associated tolerance to metabolic insult is unknown. Here, transgenic expression of tumor necrosis factor alpha induced heart failure with typical cardiac structural and energetic alterations. In this paradigm of disease remodeling, K(ATP) channels responded aberrantly to metabolic signals despite intact intrinsic channel properties, implicating defects proximal to the channel. Indeed, cardiomyocytes from failing hearts exhibited mitochondrial and creatine kinase deficits, and thus a reduced potential for metabolic signal generation and transmission. Consequently, K(ATP) channels failed to properly translate cellular distress under metabolic challenge into a protective membrane response. Failing hearts were excessively vulnerable to metabolic insult, demonstrating cardiomyocyte calcium loading and myofibrillar contraction banding, with tolerance improved by K(ATP) channel openers. Thus, disease-induced K(ATP) channel metabolic dysregulation is a contributor to the pathobiology of heart failure, illustrating a mechanism for acquired channelopathy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pinacidil prevents membrane depolarisation and intracellular Ca2+ loading in single cardiomyocytes exposed to severe metabolic stress.Int J Mol Med. 2001 Jun;7(6):639-43. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.7.6.639. Int J Mol Med. 2001. PMID: 11351278
-
Expression and function of ATP-dependent potassium channels in late post-infarction remodeling.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2007 Jun;42(6):1016-25. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2007.04.008. Epub 2007 Apr 20. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2007. PMID: 17512536
-
Mitochondrial uncoupling, with low concentration FCCP, induces ROS-dependent cardioprotection independent of KATP channel activation.Cardiovasc Res. 2006 Nov 1;72(2):313-21. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.07.019. Epub 2006 Jul 29. Cardiovasc Res. 2006. PMID: 16950237
-
ATP-sensitive potassium channels in dopaminergic neurons: transducers of mitochondrial dysfunction.News Physiol Sci. 2001 Oct;16:214-7. doi: 10.1152/physiologyonline.2001.16.5.214. News Physiol Sci. 2001. PMID: 11572924 Review.
-
Adaptive responses of vertebrate neurons to anoxia--matching supply to demand.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2006 Nov;154(1-2):226-40. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2006.03.004. Epub 2006 Mar 22. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 16621734 Review.
Cited by
-
Thioredoxin and ventricular remodeling.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2006 Nov;41(5):762-73. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2006.08.006. Epub 2006 Sep 26. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2006. PMID: 17007870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiac and vascular KATP channels in rats are activated by endogenous epoxyeicosatrienoic acids through different mechanisms.J Physiol. 2006 Sep 1;575(Pt 2):627-44. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.113985. Epub 2006 Jun 22. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16793897 Free PMC article.
-
Disrupting KATP channels diminishes the estrogen-mediated protection in female mutant mice during ischemia-reperfusion.Clin Proteomics. 2014 May 6;11(1):19. doi: 10.1186/1559-0275-11-19. eCollection 2014. Clin Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 24936167 Free PMC article.
-
Muscle KATP channels: recent insights to energy sensing and myoprotection.Physiol Rev. 2010 Jul;90(3):799-829. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00027.2009. Physiol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20664073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterogeneous upregulation of apamin-sensitive potassium currents in failing human ventricles.J Am Heart Assoc. 2013 Jan 3;2(1):e004713. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.112.004713. J Am Heart Assoc. 2013. PMID: 23525437 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham M.R., Selivanov,V.A., Hodgson,D.M., Pucar,D., Zingman,L.V., Wieringa,B., Dzeja,P.P., Alekseev,A.E. and Terzic,A. (2002) Coupling of cell energetics with membrane metabolic sensing. Integrative signaling through creatine kinase phosphotransfer disrupted by M-CK gene knock-out. J. Biol. Chem., 277, 24427–24434. - PubMed
-
- Aguilar-Bryan L., Bryan,J. and Nakazaki,M. (2001) Of mice and men: KATP channels and insulin secretion. Recent Prog. Horm. Res., 56, 47–68. - PubMed
-
- Allard B. and Lazdunski,M. (1992) Nucleotide diphosphates activate the ATP-sensitive potassium channel in mouse skeletal muscle. Pflugers Arch., 422, 185–192. - PubMed
-
- Amoroso S., Schmid-Antomarchi,H., Fosset,M. and Lazdunski,M. (1990) Glucose, sulfonylureas, and neurotransmitter release: Role of ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Science, 247, 852–854. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

