Chromatin remodeling protein Chd1 interacts with transcription elongation factors and localizes to transcribed genes
- PMID: 12682017
- PMCID: PMC154471
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg179
Chromatin remodeling protein Chd1 interacts with transcription elongation factors and localizes to transcribed genes
Abstract
Transcription in eukaryotes is influenced by the chromatin state of the template, and chromatin remodeling factors have well-documented roles in regulating transcription initiation by RNA polymerase (pol) II. Chromatin also influences transcription elongation; however, little is known about the role of chromatin remodeling factors in this process. Here, we present evidence that the Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromatin remodeling factor Chd1 functions during transcription elongation. First, we identified Chd1 in a two-hybrid screen for proteins that interact with Rtf1, a member of the Paf1 complex that associates with RNA pol II and regulates transcription elongation. Secondly, we show through co-immunoprecipitation studies that Chd1 also interacts with components of two essential elongation factors, Spt4-Spt5 and Spt16-Pob3. Thirdly, we demonstrate that deletion of CHD1 suppresses a cold-sensitive spt5 mutation that is also suppressed by defects in the Paf1 complex and RNA pol II. Finally, we demonstrate that Chd1, Rtf1 and Spt5 associate with actively transcribed regions of chromatin. Collectively, these findings suggest an important role for Chd1 and chromatin remodeling in the control of transcription elongation.
Figures
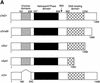







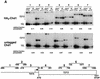

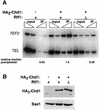
References
-
- Alén C., Kent,N.A., Jones,H.S., O’Sullivan,J., Aranda,A. and Proudfoot,N.J. (2002) A role for chromatin remodeling in transcriptional termination by RNA polymerase II. Mol. Cell, 10, 1441–1452. - PubMed
-
- Bertram M.J. and Pereira-Smith,O.M. (2001) Conservation of the MORF4 related gene family: identification of a new chromo domain subfamily and novel protein motif. Gene, 266, 111–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

