Detection of Sporothrix schenckii in clinical samples by a nested PCR assay
- PMID: 12682123
- PMCID: PMC153868
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.41.4.1414-1418.2003
Detection of Sporothrix schenckii in clinical samples by a nested PCR assay
Abstract
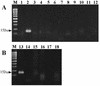
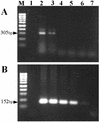
Cutaneous sporotrichosis is a chronic granulomatous fungal infection caused by Sporothrix schenckii with worldwide distribution. Its traditional diagnosis is time-consuming and difficult to differentiate from that of a clinical sporotrichoid lesion caused by various pathogens. In this study, a nested PCR assay for the detection of S. schenckii was evaluated by using a sequence of 18S rRNA gene as a target. For the examination of specificity and sensitivity, five clinical isolates with 1 ATCC 10213 strain of S. schenckii, 10 strains of clinical common fungi, 3 strains of Mycobacterium spp., Staphylococcus aureus, and normal human skin tissue were used. The expected fragment was amplified from six S. schenckii isolates in the first round and nested PCR but not from other microorganisms and human DNA. Their sequences were 100% identical to the S. schenckii 18S rRNA gene sequence deposited in GenBank. A detection limit of 40 fg of S. schenckii DNA extract was determined with ethidium bromide staining. Serial dilution studies demonstrated that the nested PCR could detect a DNA amount of 1 CFU of S. schenckii in tissue samples. We further investigated the nested PCR assay for the detection of S. schenckii from the tail tissues of 5 experimentally infected mice and from the clinical biopsy specimens of 12 patients with sporotrichosis confirmed by culture or histochemical staining. The nested PCR assay was positive in all 5 infected mice and in 11 of the 12 clinical specimens. The high sensitivity and specificity of this nested PCR indicate that the assay can provide rapid diagnosis with sufficient accuracy to be clinically useful for patients with sporotrichosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of Sporothix schenckii of various mtDNA types by nested PCR assay.Med Mycol. 2010 Feb;48(1):161-5. doi: 10.3109/13693780903117481. Med Mycol. 2010. PMID: 19626548
-
Molecular Diagnosis of Pathogenic Sporothrix Species.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015 Dec 1;9(12):e0004190. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004190. eCollection 2015 Dec. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015. PMID: 26623643 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular identification of the Sporothrix schenckii complex.Rev Iberoam Micol. 2014 Jan-Mar;31(1):2-6. doi: 10.1016/j.riam.2013.09.008. Epub 2013 Nov 19. Rev Iberoam Micol. 2014. PMID: 24270070 Review.
-
[Technical evaluation of nested PCR for the diagnosis of experimental sporotrichosis].Rev Iberoam Micol. 2012 Jul-Sep;29(3):120-5. doi: 10.1016/j.riam.2011.09.002. Epub 2011 Oct 25. Rev Iberoam Micol. 2012. PMID: 22037113 Spanish.
-
Genetic diversity of Histoplasma and Sporothrix complexes based on sequences of their ITS1-5.8S-ITS2 regions from the BOLD System.Rev Iberoam Micol. 2014 Jan-Mar;31(1):90-4. doi: 10.1016/j.riam.2013.10.003. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Rev Iberoam Micol. 2014. PMID: 24270072 Review.
Cited by
-
Sporotrichosis, Plain of Jars, Lao People's Democratic Republic.Emerg Infect Dis. 2005 Sep;11(9):1496-7. doi: 10.3201/eid1109.050240. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005. PMID: 16673522 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Rapid identification of Sporothrix species by T3B fingerprinting.J Clin Microbiol. 2012 Jun;50(6):2159-62. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00450-12. Epub 2012 Mar 7. J Clin Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22403427 Free PMC article.
-
Extracutaneous sporotrichosis.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2025 Mar 13;38(1):e0014024. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00140-24. Epub 2025 Jan 14. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2025. PMID: 39807894 Review.
-
Veterinary application of LAMP: a simple and visual detection tool for feline sporotrichosis.Braz J Microbiol. 2025 Sep;56(3):1483-1493. doi: 10.1007/s42770-025-01694-x. Epub 2025 May 28. Braz J Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40434625
-
Lymphocutaneous and nasal sporotrichosis in a dog from southern Italy: case report.Mycopathologia. 2007 Feb;163(2):75-9. doi: 10.1007/s11046-006-0086-x. Epub 2007 Feb 10. Mycopathologia. 2007. PMID: 17294354
References
-
- Aronson, N. E. 1992. Disseminated sporotrichosis. JAMA 268:2021. - PubMed
-
- Belknap, B. S. 1989. Sporotrichosis. Dermatol. Clin. 7:193-202. - PubMed
-
- Berbee, M. L., and J. W. Taylor. 1992. 18S ribosomal RNA gene sequence characters place the human pathogen Sporothrix schenckii in the genus Ophiostoma. Exp. Mycol. 16:87-91.
-
- Byrd, J., D. R. Mehregan, and D. A. Mehregan. 2001. Utility of anti-bacillus Calmette-Guerin antibodies as a screen for organisms in sporotrichoid infections. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 44:261-264. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

