Listeria monocytogenes isolates from invasive infections: variation of sero- and genotypes during an 11-year period in Finland
- PMID: 12682162
- PMCID: PMC153910
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.41.4.1694-1700.2003
Listeria monocytogenes isolates from invasive infections: variation of sero- and genotypes during an 11-year period in Finland
Abstract
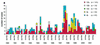
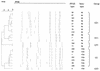
Listeria monocytogenes strains that were isolated from 314 human listeriosis cases in Finland during an 11-year period were analyzed by O:H serotyping and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). Serotyping divided the isolates into five serotypes, the most common being 1/2a (53%) and 4b (27%). During the study period, the number of cases caused by serotype 1/2a increased from 22% in 1990 to 67% in 2001, and those caused by serotype 4b decreased from 61 to 27%, respectively. PFGE with restriction enzyme AscI divided the strains into 81 PFGE genotypes; among strains of serotypes 1/2a and 4b, 49 and 18 PFGE types were seen, respectively. PFGE type 1 (serotype 1/2a) was the most prevalent single type (37 strains). Together with six other, closely related PFGE types, PFGE type 1 formed a group of 71 strains, representing 23% of all 314 strains. Strains of PFGE type 1 have also been isolated from cold smoked fish, suggesting a source of human infections caused by this type. Moreover, PFGE type 24 (serotype 1/2c) was significantly associated with gender: 5% of 180 male subjects but none of 132 female subjects (P = 0.012). An electronic database library was created from the PFGE profiles to make possible the prompt detection of new emerging profiles and the tracing of potential infection clusters in the future.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human isolates of Listeria monocytogenes in Sweden during half a century (1958-2010).Epidemiol Infect. 2014 Nov;142(11):2251-60. doi: 10.1017/S0950268813003385. Epub 2014 Jan 20. Epidemiol Infect. 2014. PMID: 24480252 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Listeria monocytogenes isolates from human listeriosis cases in Italy.J Clin Microbiol. 2009 Sep;47(9):2925-30. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00102-09. Epub 2009 Jul 15. J Clin Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19605584 Free PMC article.
-
Lineage II (Serovar 1/2a and 1/2c) Human Listeria monocytogenes Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis Types Divided into PFGE Groups Using the Band Patterns Below 145.5 kb.Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2017 Jan;14(1):8-16. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2016.2173. Epub 2016 Nov 18. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2017. PMID: 27860487
-
Semi-automated repetitive-sequence-based polymerase chain reaction compared to pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for Listeria monocytogenes subtyping.Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2010 Sep;7(9):1005-12. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2009.0450. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2010. PMID: 20528463
-
Listeria monocytogenes: Strain Heterogeneity, Methods, and Challenges of Subtyping.J Food Sci. 2015 Dec;80(12):M2868-78. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.13133. Epub 2015 Nov 20. J Food Sci. 2015. PMID: 26588067 Review.
Cited by
-
Competition of Listeria monocytogenes serotype 1/2a and 4b strains in mixed-culture biofilms.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009 Sep;75(18):5846-52. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00816-09. Epub 2009 Jul 31. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19648379 Free PMC article.
-
Listeria infection in Chinese pregnant women and neonates from Shandong.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014 Sep 15;7(9):2730-4. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014. PMID: 25356132 Free PMC article.
-
Listeria monocytogenes and Listeriosis: The Global Enigma.Foods. 2025 Apr 3;14(7):1266. doi: 10.3390/foods14071266. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40238523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human isolates of Listeria monocytogenes in Sweden during half a century (1958-2010).Epidemiol Infect. 2014 Nov;142(11):2251-60. doi: 10.1017/S0950268813003385. Epub 2014 Jan 20. Epidemiol Infect. 2014. PMID: 24480252 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and contamination patterns of Listeria monocytogenes in Pleurotus eryngii (king oyster mushroom) production plants.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jan 27;14:1064575. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1064575. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36778843 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aarnisalo, K., T. Autio, A.-M. Sjöberg, J. Lundén, H. Korkeala, and M.-L. Suihko. 2003. Typing of Listeria monocytogenes isolates originating from the food processing industry with automated ribotyping and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J. Food Prot. 66:249-255. - PubMed
-
- Allerberger, F., and S. J. Fritschel. 1999. Use of automated ribotyping of Austrian Listeria monocytogenes isolates to support epidemiological typing. J. Microbiol. Methods 35:237-244. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous. 1997. Listeriosis in England and Wales: 1983-1996. Commun. Dis. Rep. 7:95.
-
- Autio, T., J. Lunden, M. Fredriksson-Ahomaa, J. Björkroth, A.-M. Sjöberg, and H. Korkeala. 2002. Similar Listeria monocytogenes pulsotypes detected in several foods originating from different sources. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 77:83-90. - PubMed
-
- Bille, J., J. Rocourt, and B. Swaminathan. 1999. Listeria, Erysipelothrix, and Kurthia, p. 346-356. In P. R. Murray, E. J. Baron, M. A. Pfaller, F. C. Tenover, and R. H. Yolken (ed.), Manual of clinical microbiology, 7th ed. American Society of Microbiology, Washington, D.C.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

