Enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus 1R PCR assay for detection of Raoultella sp. isolates among strains identified as Klebsiella oxytoca in the clinical laboratory
- PMID: 12682174
- PMCID: PMC153902
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.41.4.1740-1742.2003
Enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus 1R PCR assay for detection of Raoultella sp. isolates among strains identified as Klebsiella oxytoca in the clinical laboratory
Abstract
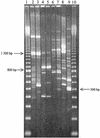
The enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus 1R PCR method, which provided recognizable profiles for reference strains of the three species of Raoultella and the two genetic groups of Klebsiella oxytoca, was applied to 19 clinical isolates identified as K. oxytoca. By this method, as confirmed by species-specific gene sequencing, two Raoultella ornithinolytica and two unclassifiable K. oxytoca isolates were identified.
Figures

References
-
- Brisse, S., and J. Verhoef. 2001. Phylogenetic diversity of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Klebsiella oxytoca clinical isolates revealed by randomly amplified polymorphic DNA, gyrA and parC genes sequencing and automated ribotyping. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 51:914-925. - PubMed
-
- Drancourt, M., C. Bollet, A. Carta, and P. Rousselier. 2001. Phylogenetic analyses of Klebsiella species delineate Klebsiella and Raoultella gen. nov., with description of Raoultella ornithinolytica comb. nov., Raoultella terrigena comb. nov. and Raoultella planticola comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 51:925-932. - PubMed
-
- Granier, S. A., L. Plaisance, V. Leflon-Guibout, E. Lagier, S. Morand, F. W. Goldstein, and M. H. Nicolas-Chanoine. 2002. Recognition of two genetic groups in Klebsiella oxytoca taxon on the basis of the chromosomal beta-lactamase and housekeeping gene sequences as well as ERIC PCR typing. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. [Online.] http://dx.doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.02408-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

