Filamin-A fragment localizes to the nucleus to regulate androgen receptor and coactivator functions
- PMID: 12682292
- PMCID: PMC153595
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0736237100
Filamin-A fragment localizes to the nucleus to regulate androgen receptor and coactivator functions
Abstract
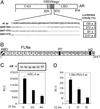
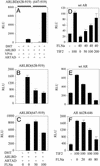
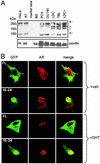
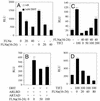
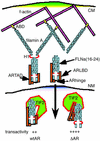
The androgen receptor (AR), a nuclear transcription factor, mediates male sexual differentiation, and its excessive action is associated with prostate cancer. We have characterized a negative regulatory domain in the AR hinge region, which interacted with filamin A (FLNa), an actin-binding cytoskeletal protein. FLNa interfered with AR interdomain interactions and competed with the coactivator transcriptional intermediary factor 2 to specifically down-regulate AR function. Although full-length FLNa was predominantly cytoplasmic, a C-terminal 100-kDa fragment of FLNa colocalized with AR to the nucleus. This naturally occurring FLNa fragment repressed AR transactivation and disrupted AR interdomain interactions and transcriptional intermediary factor 2-activated AR function in a manner reminiscent of full-length FLNa, raising the possibility that the inhibitory effects of cytoplasmic FLNa may be transduced through this fragment, which can localize to the nucleus and form part of the pre-initiation complex. This unanticipated role of FLNa adds to the growing evidence for the involvement of cytoskeletal proteins in transcription regulation.
Figures
References
-
- Wurtz J M, Bourguet W, Renaud J P, Vivat V, Chambon P, Moras D, Gronemeyer H. Nat Struct Biol. 1996;3:87–94. - PubMed
-
- Berrevoets C A, Doesburg P, Steketee K, Trapman J, Brinkmann A O. Mol Endocrinol. 1998;12:1172–1183. - PubMed
-
- He B, Kemppainen J A, Wilson E M. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:22986–22994. - PubMed
-
- Lim J, Ghadessy F J, Abdullah A A, Pinsky L, Trifiro M, Yong E L. Mol Endocrinol. 2000;14:1187–1197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

