Cripto forms a complex with activin and type II activin receptors and can block activin signaling
- PMID: 12682303
- PMCID: PMC154321
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0531290100
Cripto forms a complex with activin and type II activin receptors and can block activin signaling
Abstract
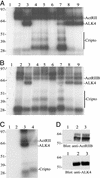
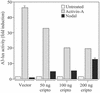
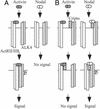
Activin, nodal, Vg1, and growth and differentiation factor 1 are members of the transforming growth factor beta superfamily and signal via the activin type II (ActRII/IIB) and type I (ALK4) serine/threonine kinase receptors. Unlike activins, however, signaling by nodal, Vg1, and growth and differentiation factor 1 requires a coreceptor from the epidermal growth factor-Cripto-FRL1-Cryptic protein family such as Cripto. Cripto has important roles during development and oncogenesis and binds nodal or related ligands and ALK4 to facilitate assembly of type I and type II receptor signaling complexes. Because Cripto mediates signaling via activin receptors and binds directly to ALK4, we tested whether transfection with Cripto would affect the ability of activin to signal and/or interact with its receptors. Here we show that Cripto can form a complex with activin and ActRII/IIB. We were unable to detect activin binding to Cripto in the absence of ActRII/IIB, indicating that unlike nodal, activin requires type II receptors to bind Cripto. If cotransfected with ActRII/IIB and ALK4, Cripto inhibited crosslinking of activin to ALK4 and the association of ALK4 with ActRII/IIB. In addition, Cripto blocked activin signaling when transfected into either HepG2 cells or 293T cells. We have also shown that under conditions in which Cripto facilitates nodal signaling, it antagonizes activin. Inhibition of activin signaling provides an additional example of a Cripto effect on the regulation of signaling by transforming growth factor-beta superfamily members. Because activin is a potent inhibitor of cell growth in multiple cell types, these results provide a mechanism that may partially explain the oncogenic action of Cripto.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cripto is a noncompetitive activin antagonist that forms analogous signaling complexes with activin and nodal.J Biol Chem. 2008 Feb 22;283(8):4490-500. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M704960200. Epub 2007 Dec 18. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18089557
-
Antibody blockade of the Cripto CFC domain suppresses tumor cell growth in vivo.J Clin Invest. 2003 Aug;112(4):575-87. doi: 10.1172/JCI17788. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 12925698 Free PMC article.
-
An activin mutant with disrupted ALK4 binding blocks signaling via type II receptors.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jul 2;279(27):28036-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M402782200. Epub 2004 Apr 27. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15123686
-
Cripto-1: a multifunctional modulator during embryogenesis and oncogenesis.Oncogene. 2005 Aug 29;24(37):5731-41. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208918. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 16123806 Review.
-
Signal transduction pathway through activin receptors as a therapeutic target of musculoskeletal diseases and cancer.Endocr J. 2008 Mar;55(1):11-21. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.kr-110. Epub 2007 Sep 14. Endocr J. 2008. PMID: 17878607 Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Activin A on Fetal Gonocytes: Chronic Versus Acute Exposure Outcomes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 May 31;13:896747. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.896747. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35721752 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous betaglycan is essential for high-potency inhibin antagonism in gonadotropes.Mol Endocrinol. 2009 Jul;23(7):1033-42. doi: 10.1210/me.2009-0021. Epub 2009 Apr 16. Mol Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19372236 Free PMC article.
-
Activins and activin antagonists in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Mar 21;14(11):1699-709. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.1699. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18350601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GRP78 and Cripto form a complex at the cell surface and collaborate to inhibit transforming growth factor beta signaling and enhance cell growth.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Jan;28(2):666-77. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01716-07. Epub 2007 Nov 8. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 17991893 Free PMC article.
-
The Activin Social Network: Activin, Inhibin, and Follistatin in Breast Development and Cancer.Endocrinology. 2019 May 1;160(5):1097-1110. doi: 10.1210/en.2019-00015. Endocrinology. 2019. PMID: 30874767 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Massagué J. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:753–791. - PubMed
-
- Piek E, Heldin C H, Ten Dijke P. FASEB J. 1999;13:2105–2124. - PubMed
-
- Matzuk M M, Kumar T R, Shou W, Coerver K A, Lau A L, Behringer R R, Finegold M J. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1996;51:123–547. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y G, Lui H M, Lin S L, Lee J M, Ying S Y. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2002;227:75–87. - PubMed
-
- Phillips D J. BioEssays. 2000;22:689–696. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

