Formation of the P1.1 pseudoknot is critical for both the cleavage activity and substrate specificity of an antigenomic trans-acting hepatitis delta ribozyme
- PMID: 12682359
- PMCID: PMC153735
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg307
Formation of the P1.1 pseudoknot is critical for both the cleavage activity and substrate specificity of an antigenomic trans-acting hepatitis delta ribozyme
Abstract
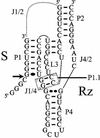
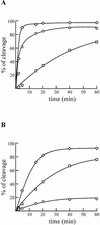
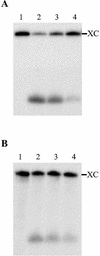
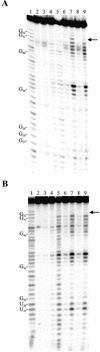
Hepatitis delta virus RNAs possess self-cleavage activities that produce 2',3'-cyclic phosphate and 5'-hydroxyl termini (i.e. cis-acting delta ribozyme). Trans-acting delta ribozymes have been engineered by removing a junction from the cis version, thereby producing one molecule possessing the substrate sequence and the other the catalytic domain. According to the pseudoknot model, the secondary structure of the delta ribozyme includes a pseudoknot (i.e. P1.1 stem) formed by two base pairs from residues of the L3 loop and J1/4 junction. A collection of 48 P1.1 stem mutants was synthesized in order to provide an original characterization of both the importance and the structure of this pseudoknot in a trans-acting version of the ribozyme. Several structural differences were noted compared to the results reported for cis-acting ribozymes. For example, a combination of two stable Watson-Crick base pairs composing the essential P1.1 stem was demonstrated to be crucial for a significant level of activity, while the cis version required only one base pair. In addition, we present the first physical evidences revealing that the composition of the P1.1 stem affects the substrate specificity for ribozyme cleavage. Depending on the residues forming the J1/4 junction, non-productive ribozyme-substrate complexes can be observed. This phenomenon is proposed to be important for further development of a gene-inactivation system based on delta ribozyme.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A nested double pseudoknot is required for self-cleavage activity of both the genomic and antigenomic hepatitis delta virus ribozymes.RNA. 1999 Jun;5(6):720-7. doi: 10.1017/s1355838299990209. RNA. 1999. PMID: 10376872 Free PMC article.
-
A novel structural rearrangement of hepatitis delta virus antigenomic ribozyme.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(20):6820-31. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm674. Epub 2007 Oct 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17933779 Free PMC article.
-
Terbium-mediated footprinting probes a catalytic conformational switch in the antigenomic hepatitis delta virus ribozyme.J Mol Biol. 2004 Aug 6;341(2):389-403. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.05.074. J Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15276831
-
Self-cleaving ribozymes of hepatitis delta virus RNA.Eur J Biochem. 1997 Aug 1;247(3):741-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.00741.x. Eur J Biochem. 1997. PMID: 9288893 Review.
-
Ribozyme activity in the genomic and antigenomic RNA strands of hepatitis delta virus.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2002 Jan;59(1):112-25. doi: 10.1007/s00018-002-8409-7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2002. PMID: 11846024 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gene targeting in the Gram-Positive bacterium Lactococcus lactis, using various delta ribozymes.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006 Jan;72(1):869-79. doi: 10.1128/AEM.72.1.869-879.2006. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16391129 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterization of the SOFA delta ribozyme.RNA. 2005 Dec;11(12):1858-68. doi: 10.1261/rna.2112705. Epub 2005 Oct 26. RNA. 2005. PMID: 16251383 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating RNA structure and catalysis: lessons from small cleaving ribozymes.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009 Dec;66(24):3937-50. doi: 10.1007/s00018-009-0124-1. Epub 2009 Aug 30. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 19718544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ribozyme-based gene-inactivation systems require a fine comprehension of their substrate specificities; the case of delta ribozyme.Curr Med Chem. 2003 Dec;10(23):2589-97. doi: 10.2174/0929867033456486. Curr Med Chem. 2003. PMID: 14529473 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the mechanical unfolding of RNA pseudoknots.J Mol Biol. 2008 Jan 11;375(2):511-28. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.05.058. Epub 2007 May 26. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18021801 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mercure S., Lafontaine,D., Roy,G. and Perreault,J.P. (1997) Le motif autocatalytique d’ARN du virus delta de l’hépatite humaine. Médecine/Science, 13, 662–667.
-
- Shih I.H. and Been,M.D. (2002) Catalytic strategies of the hepatitis delta virus ribozymes. Annu. Rev. Biochem., 71, 887–917. - PubMed
-
- Doherty E.A. and Doudna,J.A. (2000) Ribozyme structure and mechanism. Annu. Rev. Biochem., 69, 597–615. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

