Novel small-molecule inhibitors of RNA polymerase III
- PMID: 12684375
- PMCID: PMC154847
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.2.2.256-264.2003
Novel small-molecule inhibitors of RNA polymerase III
Abstract
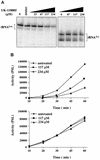
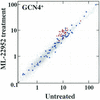
A genetic approach utilizing the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae was used to identify the target of antifungal compounds. This analysis led to the identification of small molecule inhibitors of RNA polymerase (Pol) III from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Three lines of evidence show that UK-118005 inhibits cell growth by targeting RNA Pol III in yeast. First, a dominant mutation in the g domain of Rpo31p, the largest subunit of RNA Pol III, confers resistance to the compound. Second, UK-118005 rapidly inhibits tRNA synthesis in wild-type cells but not in UK-118005 resistant mutants. Third, in biochemical assays, UK-118005 inhibits tRNA gene transcription in vitro by the wild-type but not the mutant Pol III enzyme. By testing analogs of UK-118005 in a template-specific RNA Pol III transcription assay, an inhibitor with significantly higher potency, ML-60218, was identified. Further examination showed that both compounds are broad-spectrum inhibitors, displaying activity against RNA Pol III transcription systems derived from Candida albicans and human cells. The identification of these inhibitors demonstrates that RNA Pol III can be targeted by small synthetic molecules.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Inhibition of tRNA Gene Transcription by the Immunosuppressant Mycophenolic Acid.Mol Cell Biol. 2019 Dec 11;40(1):e00294-19. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00294-19. Print 2019 Dec 11. Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31658995 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterization of Polr3a hypomyelinating leukodystrophy mutations in the S. cerevisiae homolog, RPC160.Gene. 2021 Feb 5;768:145259. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.145259. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Gene. 2021. PMID: 33148458 Free PMC article.
-
Maf1p, a negative effector of RNA polymerase III in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Aug;21(15):5031-40. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.15.5031-5040.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11438659 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the RNA polymerase III transcription machinery in Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and human.Nucleic Acids Res. 2001 Jul 1;29(13):2675-90. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.13.2675. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001. PMID: 11433012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maf1, a general negative regulator of RNA polymerase III in yeast.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Mar-Apr;1829(3-4):376-84. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.11.004. Epub 2012 Nov 28. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23201230 Review.
Cited by
-
Zooming in: PAGE-Northern Blot Helps to Analyze Anti-Sense Transcripts Originating from Human rIGS under Transcriptional Stress.Noncoding RNA. 2021 Aug 24;7(3):50. doi: 10.3390/ncrna7030050. Noncoding RNA. 2021. PMID: 34449671 Free PMC article.
-
An evolutionary approach uncovers a diverse response of tRNA 2-thiolation to elevated temperatures in yeast.RNA. 2015 Feb;21(2):202-12. doi: 10.1261/rna.048199.114. Epub 2014 Dec 12. RNA. 2015. PMID: 25505025 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of host cytosolic sensors and bacterial factors regulating the type I interferon response to Legionella pneumophila.PLoS Pathog. 2009 Nov;5(11):e1000665. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000665. Epub 2009 Nov 20. PLoS Pathog. 2009. PMID: 19936053 Free PMC article.
-
The nuclear and cytoplasmic activities of RNA polymerase III, and an evolving transcriptome for surveillance.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Dec 2;49(21):12017-12034. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab1145. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34850129 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancer SINEs Link Pol III to Pol II Transcription in Neurons.Cell Rep. 2017 Dec 5;21(10):2879-2894. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.11.019. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 29212033 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams, A., D. E. Gottschling, C. A. Kaiser, and T. Stearns. 1997. Methods in yeast genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, N.Y.
-
- Allison, L. A., M. Moyle, M. Shales, and C. J. Ingles. 1985. Extensive homology among the largest subunits of eukaryotic RNA polymerases. Cell 42:599-610. - PubMed
-
- Brachmann, C. B., A. Davies, G. J. Cost, E. Caputo, J. Li, P. Hieter, and J. D. Boeke. 1998. Designer deletion strains derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C: a useful set of strains and plasmids for PCR-mediated gene disruption and other applications. Yeast 14:115-132. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

