TUC-4b, a novel TUC family variant, regulates neurite outgrowth and associates with vesicles in the growth cone
- PMID: 12684468
- PMCID: PMC6742060
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-07-02815.2003
TUC-4b, a novel TUC family variant, regulates neurite outgrowth and associates with vesicles in the growth cone
Abstract
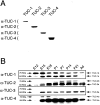
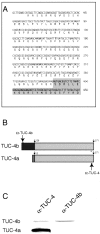
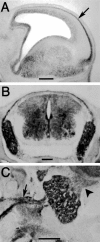
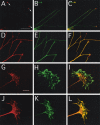
The TUC (TOAD-64/Ulip/CRMP) proteins are homologs of UNC-33, a protein that is required for axon extension and guidance in Caenorhabditis elegans. The TUC proteins are expressed in newly born neurons in the developing nervous system and have been implicated in semaphorin signaling and neuronal polarity. Here, we identify several new variants of the TUC family, each of which is expressed during distinct periods of neural development. We cloned and characterized TUC-4b, a variant of TUC-4a that includes a unique N-terminal extension. The functional relevance of this N-terminal domain is demonstrated by the finding that overexpression of TUC-4b, but not TUC-4a, results in increased neurite length and branching. Furthermore, whereas TUC-4a is expressed throughout life, TUC-4b is expressed exclusively during embryonic development. TUC-4b is localized to SV2 (synaptic vesicle protein 2)-positive vesicles in the central domain of the growth cone, suggesting a potential role in growth cone vesicle transport. Furthermore, TUC-4b interacts with the SH3A (Src homology 3A) domain of intersectin, an endocytic-exocytic adaptor protein. Together, these data suggest that TUC-4b can regulate neurite extension and branching through a mechanism that may involve membrane transport in the growth cone.
Figures
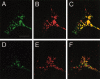
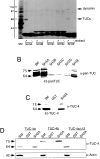
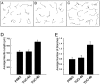
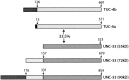
References
-
- Bouchard JF, Roux PP, Shekarbi M, Barker PA, Kennedy TE. cAMP elevation rapidly translocates DCC to the plasma membrane and promotes netrin-1-dependent axon extension. Soc Neurosci Abstr. 2002;28:729.14.
-
- Bunge MB. Initial endocytosis of peroxidase or ferritin by growth cones of cultured nerve cells. J Neurocytol. 1977;6:407–439. - PubMed
-
- Byk T, Ozon S, Sobel A. The Ulip family phosphoproteins—common and specific properties. Eur J Biochem. 1998;254:14–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
