Circadian and photic regulation of phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and Elk-1 in the suprachiasmatic nuclei of the Syrian hamster
- PMID: 12684495
- PMCID: PMC6742114
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-07-03085.2003
Circadian and photic regulation of phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and Elk-1 in the suprachiasmatic nuclei of the Syrian hamster
Abstract
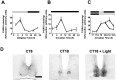
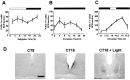
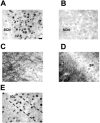
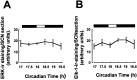
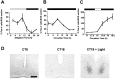
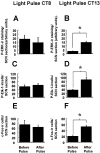
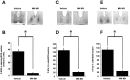
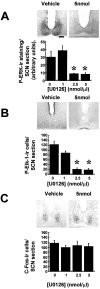
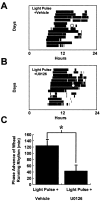
In this study we investigated the circadian and photic regulation of phosphorylation of the extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) 1/2, and the transcription factor Elk-1 in the suprachiasmatic nuclei of the Syrian hamster. We report that levels of phosphorylated ERK (P-ERK) are rhythmic, peaking during the mid subjective day, whereas phosphorylated Elk-1 (P-Elk-1) shows no distinct rhythm. Light pulses during the subjective night rapidly, but transiently, induce P-ERK, whereas P-Elk-1 is also induced, albeit with a slower time course. Application of the ERK pathway inhibitor U0126 attenuates photic induction of both P-ERK and P-Elk-1 and phase advances of wheel-running behavior. The NMDA receptor channel blocker, MK-801, also significantly attenuates photic induction of P-ERK and P-Elk-1. Taken together, these results indicate a role of the ERK cascade in the regulation of free-running circadian rhythms and of photic-resetting of these rhythms and suggest that in the mammalian suprachiasmatic nuclei, Elk-1 represents a novel molecular component of the photic-induction pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dark pulse suppression of P-ERK and c-Fos in the hamster suprachiasmatic nuclei.Eur J Neurosci. 2005 Jul;22(1):158-68. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04193.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16029205
-
Non-photic phase shifting of the circadian clock: role of the extracellular signal-responsive kinases I/II/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway.Eur J Neurosci. 2008 Dec;28(12):2511-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06533.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19087176
-
Nerve growth factor-induced circadian phase shifts and MAP kinase activation in the hamster suprachiasmatic nuclei.Eur J Neurosci. 2005 Aug;22(3):665-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04247.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16101748
-
Convergence of the SUMO and MAPK pathways on the ETS-domain transcription factor Elk-1.Biochem Soc Symp. 2006;(73):121-9. doi: 10.1042/bss0730121. Biochem Soc Symp. 2006. PMID: 16626293 Review.
-
SUMO and transcriptional repression: dynamic interactions between the MAP kinase and SUMO pathways.Cell Cycle. 2003 Nov-Dec;2(6):528-30. doi: 10.4161/cc.2.6.597. Cell Cycle. 2003. PMID: 14504467 Review.
Cited by
-
Light stimulates MSK1 activation in the suprachiasmatic nucleus via a PACAP-ERK/MAP kinase-dependent mechanism.J Neurosci. 2005 Jun 1;25(22):5305-13. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4361-04.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15930378 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin signaling modulates photic entrainment of the suprachiasmatic circadian clock.J Neurosci. 2010 May 5;30(18):6302-14. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5482-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20445056 Free PMC article.
-
Photic regulation of map kinase phosphatases MKP1/2 and MKP3 in the hamster suprachiasmatic nuclei.J Mol Neurosci. 2008 Feb;34(2):187-92. doi: 10.1007/s12031-007-9021-y. Epub 2007 Dec 5. J Mol Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18058073
-
The circadian clock modulates core steps in long-term memory formation in Aplysia.J Neurosci. 2006 Aug 23;26(34):8662-71. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2307-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16928854 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Kinases in the Photic Signaling of the Mammalian Circadian Clock.Yale J Biol Med. 2019 Jun 27;92(2):241-250. eCollection 2019 Jun. Yale J Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 31249485 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abe H, Rusak B, Robertson HA. Photic induction of Fos protein in the suprachiasmatic nucleus is inhibited by the NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801. Neurosci Lett. 1991;127:9–12. - PubMed
-
- Adams JP, Sweatt JD. Molecular psychology: roles for the ERK MAP kinase cascade in memory. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2002;42:135–163. - PubMed
-
- Allada R, Emery P, Takahashi JS, Rosbash M. Stopping time: the genetics of fly and mouse circadian clocks. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2001;24:1091–1119. - PubMed
-
- Arima H, House SB, Gainer H, Aguilera G. Neuronal activity is required for the circadian rhythm of vasopressin gene transcription in the suprachiasmatic nucleus in vitro. Endocrinology. 2002;143:4165–4171. - PubMed
-
- Butcher G, Dziema H, Collamore M, Burgoon PW, Obrietan K. The p42/44 MAP kinase pathway couples photic input to circadian clock entrainment. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:29519–29525. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
