Phage HK022 Nun protein represses translation of phage lambda N (transcription termination/translation repression)
- PMID: 12684530
- PMCID: PMC154341
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0430995100
Phage HK022 Nun protein represses translation of phage lambda N (transcription termination/translation repression)
Abstract
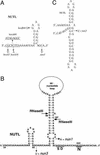
The N-terminal arginine-rich motif of phage HK022 Nun protein binds to NUT sequences in phage lambda nascent transcripts and induces transcription termination. Interactions between the Nun C terminus and RNA polymerase as well as the DNA template are required for termination. We have isolated Nun C-terminal point and deletion mutants that are unable to block transcription. The mutants bind NUT RNA and inhibit translation of the lambda N gene. Thus HK022 excludes lambda both by terminating transcription on the phage chromosome and by preventing translation of the essential lambda N gene. Like N autoregulation, translation repression by Nun requires host RNaseIII deficiency (rnc) or a mutation in the RNaseIII processing site (rIII) located between NUTL and the beginning of the N coding sequence. Our data support the idea that Nun bound at NUTL causes steric interference with ribosome attachment to the nearby N coding sequence. Two models, Nun acting alone or in complex with host proteins, are discussed.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

