Assembly of high-affinity insulin receptor agonists and antagonists from peptide building blocks
- PMID: 12684539
- PMCID: PMC153573
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0830026100
Assembly of high-affinity insulin receptor agonists and antagonists from peptide building blocks
Abstract
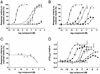
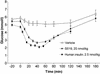
Insulin is thought to elicit its effects by crosslinking the two extracellular alpha-subunits of its receptor, thereby inducing a conformational change in the receptor, which activates the intracellular tyrosine kinase signaling cascade. Previously we identified a series of peptides binding to two discrete hotspots on the insulin receptor. Here we show that covalent linkage of such peptides into homodimers or heterodimers results in insulin agonists or antagonists, depending on how the peptides are linked. An optimized agonist has been shown, both in vitro and in vivo, to have a potency close to that of insulin itself. The ability to construct such peptide derivatives may offer a path for developing agonists or antagonists for treatment of a wide variety of diseases.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A novel high-affinity peptide antagonist to the insulin receptor.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008 Nov 14;376(2):380-3. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.08.151. Epub 2008 Sep 7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008. PMID: 18782558
-
Shortened insulin analogues: marked changes in biological activity resulting from replacement of TyrB26 and N-methylation of peptide bonds in the C-terminus of the B-chain.Biochemistry. 2004 Mar 2;43(8):2323-31. doi: 10.1021/bi036001w. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 14979729
-
In vitro phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 by protein kinase C-zeta: functional analysis and identification of novel phosphorylation sites.Biochemistry. 2004 May 18;43(19):5888-901. doi: 10.1021/bi049640v. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15134463
-
Relaxin-3, INSL5, and their receptors.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2008;46:213-37. doi: 10.1007/400_2007_055. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2008. PMID: 18236022 Review.
-
[Introduction of mutations in insulin molecule: positive and negative mutations].Biomed Khim. 2014 Jul-Aug;60(4):430-7. doi: 10.18097/pbmc20146004430. Biomed Khim. 2014. PMID: 25249526 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Insulin receptor (IR) and insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGF-1R) signaling systems: novel treatment strategies for cancer.Med Oncol. 2014 Jan;31(1):805. doi: 10.1007/s12032-013-0805-3. Epub 2013 Dec 14. Med Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24338270 Review.
-
Regulation and function of insulin and insulin-like growth factor receptor signalling.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2025 Jul;26(7):558-580. doi: 10.1038/s41580-025-00826-3. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 39930003 Review.
-
Functional selectivity of insulin receptor revealed by aptamer-trapped receptor structures.Nat Commun. 2022 Oct 30;13(1):6500. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34292-8. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36310231 Free PMC article.
-
Agonism and antagonism at the insulin receptor.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51972. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051972. Epub 2012 Dec 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23300584 Free PMC article.
-
eEF1A1 binds and enriches protoporphyrin IX in cancer cells in 5-aminolevulinic acid based photodynamic therapy.Sci Rep. 2016 May 6;6:25353. doi: 10.1038/srep25353. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27150264 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hubbard S R, Wei L, Ellis L, Hendrickson W A. Nature. 1994;372:746–754. - PubMed
-
- Garrett T J, McKern N M, Lou M Z, Frenkel M J, Bentley J D, Lovrecz G O, Elleman T C, Cosgrove L J, Ward C W. Nature. 1998;394:395–399. - PubMed
-
- Schäffer L. Eur J Biochem. 1994;221:1127–1132. - PubMed
-
- De Meyts P. Diabetologia. 1994;37:S135–S148. - PubMed
-
- Pillutla R C, Hsiao K C, Beasley J R, Brandt J, Østergaard S, Hansen P H, Spetzler J C, Danielsen G M, Andersen A S, Brissette R E, et al. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:22590–22594. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

