Eggshell and egg yolk proteins in fish: hepatic proteins for the next generation: oogenetic, population, and evolutionary implications of endocrine disruption
- PMID: 12685931
- PMCID: PMC153486
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-5926-2-4
Eggshell and egg yolk proteins in fish: hepatic proteins for the next generation: oogenetic, population, and evolutionary implications of endocrine disruption
Abstract
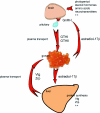
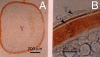
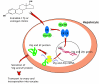
The oocyte is the starting point for a new generation. Most of the machinery for DNA and protein synthesis needed for the developing embryo is made autonomously by the fertilized oocyte. However, in fish and in many other oviparous vertebrates, the major constituents of the egg, i.e. yolk and eggshell proteins, are synthesized in the liver and transported to the oocyte for uptake. Vitellogenesis, the process of yolk protein (vitellogenin) synthesis, transport, and uptake into the oocyte, and zonagenesis, the synthesis of eggshell zona radiata proteins, their transport and deposition by the maturing oocyte, are important aspects of oogenesis. The many molecular events involved in these processes require tight, coordinated regulation that is under strict endocrine control, with the female sex steroid hormone estradiol-17beta in a central role. The ability of many synthetic chemical compounds to mimic this estrogen can lead to unscheduled hepatic synthesis of vitellogenin and zona radiata proteins, with potentially detrimental effects to the adult, the egg, the developing embryo and, hence, to the recruitment to the fish population. This has led to the development of specific and sensitive assays for these proteins in fish, and the application of vitellogenin and zona radiata proteins as informative biomarkers for endocrine disrupting effects of chemicals and effluents using fish as test organisms. The genes encoding these important reproductive proteins are conserved in the animal kingdom and are products of several hundred million years of evolution.
Figures
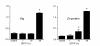
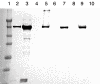


Similar articles
-
Oogenesis in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) occurs by zonagenesis preceding vitellogenesis in vivo and in vitro.J Endocrinol. 1998 Aug;158(2):259-66. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1580259. J Endocrinol. 1998. PMID: 9771470
-
Differential sensitivity of zonagenesis and vitellogenesis in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L) to DDT pesticides.J Exp Zool. 1998 Jul 1;281(4):346-53. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-010x(19980701)281:4<346::aid-jez9>3.0.co;2-o. J Exp Zool. 1998. PMID: 9658595
-
Eggshell zona radiata-proteins from cod (Gadus morhua): extra-ovarian origin and induction by estradiol-17 beta.Int J Dev Biol. 1992 Jun;36(2):247-54. Int J Dev Biol. 1992. PMID: 1525012
-
Molecular markers of endocrine disruption in aquatic organisms.J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2003 Sep-Oct;6(5):453-96. doi: 10.1080/10937400306476. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2003. PMID: 12888444 Review.
-
Oogenesis and egg development in triatomines: a biochemical approach.An Acad Bras Cienc. 2005 Sep;77(3):405-30. doi: 10.1590/s0001-37652005000300005. Epub 2005 Aug 24. An Acad Bras Cienc. 2005. PMID: 16127549 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of dopamine 2 receptor antagonist on sex steroid levels, oocyte maturation and spawning performances in Waigieu seaperch (Psammoperca waigiensis).Fish Physiol Biochem. 2013 Apr;39(2):403-11. doi: 10.1007/s10695-012-9708-z. Epub 2012 Aug 22. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2013. PMID: 22911104
-
MnHSP90 cDNA characterization and its expression during the ovary development in oriental river prawn, Macrobrachium nipponense.Mol Biol Rep. 2011 Feb;38(2):1399-406. doi: 10.1007/s11033-010-0243-7. Epub 2010 Jul 31. Mol Biol Rep. 2011. PMID: 20680464
-
Vitamin E deficiency decreases long-chain PUFA in zebrafish (Danio rerio).J Nutr. 2011 Dec;141(12):2113-8. doi: 10.3945/jn.111.144279. Epub 2011 Oct 19. J Nutr. 2011. PMID: 22013196 Free PMC article.
-
17β-Estradiol Induced Sex Reversal and Gonadal Transcriptome Analysis in the Oriental River Prawn (Macrobrachium nipponense): Mechanisms, Pathways, and Potential Harm.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 9;24(10):8481. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108481. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37239827 Free PMC article.
-
The Plasticizer Bisphenol A Perturbs the Hepatic Epigenome: A Systems Level Analysis of the miRNome.Genes (Basel). 2017 Oct 13;8(10):269. doi: 10.3390/genes8100269. Genes (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29027980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tyler CR, Sumpter JP. Oocyte growth and development in teleost. Rev Fish Biol Fisheries. 1996;6:287–318.
-
- Selman K, Wallace RA. Cellular aspects of oocyte growth in teleosts. Zool Sci. 1989;6:211–231.
-
- Schneider WJ. Vitellogenin receptors: oocyte-specific members of the low-density lipoprotein receptor supergene family. Int Rev Cytol. 1996;166:103–137. - PubMed
-
- Guraya SS. The cell and molecular biology of fish oogenesis. Monogr Dev Biol. 1986;18:1–223. - PubMed
-
- Hoar WS. Reproduction. In: Hoar WS, Randall DJ, editor. Fish Physiology. III. New York, Academic Press; 1969. p. Chapter 1.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
