Nestin promotes the phosphorylation-dependent disassembly of vimentin intermediate filaments during mitosis
- PMID: 12686602
- PMCID: PMC153115
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-08-0545
Nestin promotes the phosphorylation-dependent disassembly of vimentin intermediate filaments during mitosis
Abstract
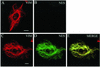
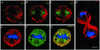
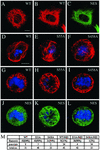
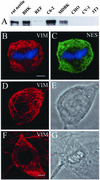
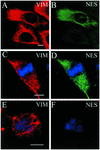
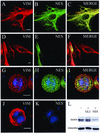
The expression of the intermediate filament (IF) protein nestin is closely associated with rapidly proliferating progenitor cells during neurogenesis and myogenesis, but little is known about its function. In this study, we examine the effects of nestin expression on the assembly state of vimentin IFs in nestin-free cells. Nestin is introduced by transient transfection and is positively correlated with the disassembly of vimentin IFs into nonfilamentous aggregates or particles in mitotic but not interphase cells. This nestin-mediated disassembly of IFs is dependent on the phosphorylation of vimentin by the maturation/M-phase-promoting factor at ser-55 in the amino-terminal head domain. In addition, the disassembly of vimentin IFs during mitosis appears to be a unique feature of nestin-expressing cell types. Furthermore, when the expression of nestin is downregulated by the nestin-specific small interfering RNA in nestin-expressing cells, vimentin IFs remain assembled throughout all stages of mitosis. Previous studies suggest that nonfilamentous vimentin particles are IF precursors and can be transported rapidly between different cytoplasmic compartments along microtubule tracks. On the basis of these observations, we speculate that nestin may play a role in the trafficking and distribution of IF proteins and potentially other cellular factors to daughter cells during progenitor cell division.
Figures

References
-
- Aubin JE, Osborn M, Franke WW, Weber K. Intermediate filaments of the vimentin-type and the cytokeratin-type are distributed differently during mitosis. Exp Cell Res. 1980;129:149–165. - PubMed
-
- Bellin RM, Sernett SW, Becker B, Ip W, Huiatt TW, Robson RM. Molecular characteristics and interactions of the intermediate filament protein synemin: interactions with alpha-actinin may anchor synemin-containing heterofilaments. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:29493–29499. - PubMed
-
- Chou YH, Bischoff JR, Beach D, Goldman RD. Intermediate filament reorganization during mitosis is mediated by p34cdc2 phosphorylation of vimentin. Cell. 1990;62:1063–1071. - PubMed
-
- Chou YH, Opal P, Quinlan RA, Goldman RD. The relative roles of specific N- and C-terminal phosphorylation sites in the disassembly of intermediate filament in mitotic BHK-21 cells. J Cell Sci. 1996;109:817–826. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

