Mutations of MYO6 are associated with recessive deafness, DFNB37
- PMID: 12687499
- PMCID: PMC1180285
- DOI: 10.1086/375122
Mutations of MYO6 are associated with recessive deafness, DFNB37
Abstract
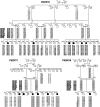
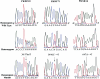
Cosegregation of profound, congenital deafness with markers on chromosome 6q13 in three Pakistani families defines a new recessive deafness locus, DFNB37. Haplotype analyses reveal a 6-cM linkage region, flanked by markers D6S1282 and D6S1031, that includes the gene encoding unconventional myosin VI. In families with recessively inherited deafness, DFNB37, our sequence analyses of MYO6 reveal a frameshift mutation (36-37insT), a nonsense mutation (R1166X), and a missense mutation (E216V). These mutations, along with a previously published missense allele linked to autosomal dominant progressive hearing loss (DFNA22), provide an allelic spectrum that probes the relationship between myosin VI dysfunction and the resulting phenotype.
Figures

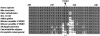
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Center for Medical Genetics, Marshfield Medical Research Foundation, http://research.marshfieldclinic.org/genetics/
-
- Hereditary Hearing Loss Homepage, http://www.uia.ac.be/dnalab/hhh/
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for MYO6 [accession number AB002387])
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for DFNA22) - PubMed
-
- Primer3 Web-Based Server, http://www.genome.wi.mit.edu/cgi-bin/primer/primer3_www.cgi
References
-
- Ahituv N, Sobe T, Robertson NG, Morton CC, Taggart RT, Avraham KB (2000) Genomic structure of the human unconventional myosin VI gene. Gene 261:269–275 - PubMed
-
- Avraham KB, Hasson T, Sobe T, Balsara B, Testa JR, Skvorak AB, Morton CC, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA (1997) Characterization of unconventional MYO6, the human homologue of the gene responsible for deafness in Snell’s waltzer mice. Hum Mol Genet 6:1225–1231 - PubMed
-
- Avraham KB, Hasson T, Steel KP, Kingsley DM, Russell LB, Mooseker MS, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA (1995) The mouse Snell’s waltzer deafness gene encodes an unconventional myosin required for structural integrity of inner ear hair cells. Nat Genet 11:369–375 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

