Defective CD8 T cell memory following acute infection without CD4 T cell help
- PMID: 12690202
- PMCID: PMC2778341
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1083317
Defective CD8 T cell memory following acute infection without CD4 T cell help
Abstract
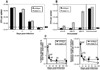
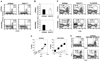
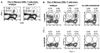
The CD8+ cytotoxic T cell response to pathogens is thought to be CD4+ helper T cell independent because infectious agents provide their own inflammatory signals. Mice that lack CD4+ T cells mount a primary CD8 response to Listeria monocytogenes equal to that of wild-type mice and rapidly clear the infection. However, protective memory to a challenge is gradually lost in the former animals. Memory CD8+ T cells from normal mice can respond rapidly, but memory CD8+ T cells that are generated without CD4 help are defective in their ability to respond to secondary encounters with antigen. The results highlight a previously undescribed role for CD4 help in promoting protective CD8 memory development.
Figures
Comment in
-
Immunology. CD8 T cells remember with a little help.Science. 2003 Apr 11;300(5617):263-5. doi: 10.1126/science.1084511. Science. 2003. PMID: 12690179 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bennett SR, et al. Nature. 1998;393:478. - PubMed
-
- Schoenberger SP, Toes RE, van der Voort EI, Offringa R, Melief CJ. Nature. 1998;393:480. - PubMed
-
- Ridge JP, Di Rosa F, Matzinger P. Nature. 1998;393:474. - PubMed
-
- Janeway CA, Jr, Medzhitov R. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002;20:197. - PubMed
-
- Gordon S. Cell. 2002;111:927. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

