Close relationship between autoimmune pancreatitis and multifocal fibrosclerosis
- PMID: 12692053
- PMCID: PMC1773660
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.52.5.683
Close relationship between autoimmune pancreatitis and multifocal fibrosclerosis
Abstract
Background: Autoimmune pancreatitis is a unique clinical entity proposed recently, and is sometimes associated with inflammation of other organs.
Aims: To examine the pathophysiology of the pancreas and other organs in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis.
Patients and methods: We evaluated clinicopathological findings in six resected and one autopsied patient with autoimmune pancreatitis. The pancreas, peripancreatic tissue, bile duct, and gall bladder were examined histologically and immunohistochemically. Biopsied salivary gland and cervical lymph node of one patient were also examined. We also performed similar immunohistochemical examinations in pancreatectomy specimens from 10 patients with alcoholic chronic pancreatitis and biopsied salivary glands from five patients with Sjögren's syndrome.
Results: Stenosis of the extrahepatic bile duct was detected in all patients. Histological findings were characterised by diffuse lymphoplasmacytic infiltration with marked interstitial fibrosis and acinar atrophy, obliterated phlebitis of the pancreatic veins, and involvement of the portal vein. Immunohistochemically, diffusely infiltrating cells consisted predominantly of CD4 or CD8 positive T lymphocytes and IgG4 positive plasma cells. Similar inflammatory processes also involved the peripancreatic tissue, extrahepatic bile duct, gall bladder, and salivary gland. Lymph nodes were swollen with infiltration of IgG4 positive plasma cells. None of these findings was seen in alcoholic chronic pancreatitis or Sjögren's syndrome.
Conclusions: The development of the specific inflammations in extensive organs as well as the pancreas in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis strongly suggests a close relationship between autoimmune pancreatitis and multifocal fibrosclerosis.
Figures

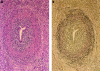

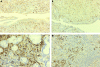
Comment in
-
Primary antiphospholipid syndrome as a new cause of autoimmune pancreatitis.Gut. 2004 Mar;53(3):468; author reply 468. Gut. 2004. PMID: 14960537 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Interstitial pneumonia associated with autoimmune pancreatitis.Gut. 2004 May;53(5):770; author reply 770-1. Gut. 2004. PMID: 15082601 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Sarles H, Sarles JC, Muratore R, et al. Chronic inflammatory sclerosis of the pancreas—An autonomous pancreatic disease? Am J Dig Dis 1961;6:688–98. - PubMed
-
- Sarles H, Muratore R, Sarles JC, et al. Aetiology and pathology of chronic pancreatitis. Bibl Gastroenterol 1965;7:75–120.
-
- Nakano S, Takeda I, Kitamura K, et al.Vanishing tumor of the abdomen in patient with Sjögren’s syndrome. Am J Dis 1978;23:75–9S.
-
- Antal L, Kavai M, Szabo G, et al. Immunological investigations in acute chronic pancreatitis. Digestion 1980;20:100–5. - PubMed
-
- Yoshida K, Toki F, Takeuchi T, et al. Chronic pancreatitis caused by autoimmune abnormality. Proposal of concept of autoimmune pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci 1995;40:1561–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
