Epithelial contact guidance on well-defined micro- and nanostructured substrates
- PMID: 12692189
- PMCID: PMC1885893
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.00383
Epithelial contact guidance on well-defined micro- and nanostructured substrates
Abstract
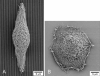
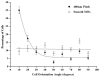
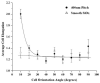
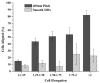
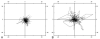
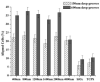
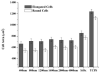
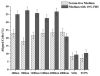
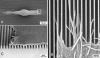
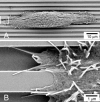
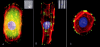
The human corneal basement membrane has a rich felt-like surface topography with feature dimensions between 20 nm and 200 nm. On the basis of these findings, we designed lithographically defined substrates to investigate whether nanotopography is a relevant stimulus for human corneal epithelial cells. We found that cells elongated and aligned along patterns of grooves and ridges with feature dimensions as small as 70 nm, whereas on smooth substrates, cells were mostly round. The percentage of aligned cells was constant on substrate tomographies with lateral dimensions ranging from the nano- to the micronscale, and increased with groove depth. The presence of serum in the culture medium resulted in a larger percentage of cells aligning along the topographic patterns than when no serum was added to the basal medium. When present, actin microfilaments and focal adhesions were aligned along the substrate topographies. The width of the focal adhesions was determined by the width of the ridges in the underlying substrate. This work documents that biologic length-scale topographic features that model features encountered in the native basement membrane can profoundly affect epithelial cell behavior.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Biological length scale topography enhances cell-substratum adhesion of human corneal epithelial cells.J Cell Sci. 2004 Jul 1;117(Pt 15):3153-64. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01146. J Cell Sci. 2004. PMID: 15226393 Free PMC article.
-
Responses of human keratocytes to micro- and nanostructured substrates.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2004 Dec 1;71(3):369-76. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.30089. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2004. PMID: 15470741
-
The effect of environmental factors on the response of human corneal epithelial cells to nanoscale substrate topography.Biomaterials. 2006 Jul;27(21):3945-54. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.01.044. Epub 2006 Mar 30. Biomaterials. 2006. PMID: 16580065 Free PMC article.
-
Is there a universal mechanism of cell alignment in response to substrate topography?Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2021 Jun;78(6):284-292. doi: 10.1002/cm.21661. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2021. PMID: 33843154 Review.
-
Effects of synthetic micro- and nano-structured surfaces on cell behavior.Biomaterials. 1999 Mar;20(6):573-88. doi: 10.1016/s0142-9612(98)00209-9. Biomaterials. 1999. PMID: 10213360 Review.
Cited by
-
Real-Time Impedance Monitoring of Epithelial Cultures with Inkjet-Printed Interdigitated-Electrode Sensors.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Oct 8;20(19):5711. doi: 10.3390/s20195711. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33049961 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of a bilayered, micropatterned hydrogel dressing for full-thickness wound healing.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016 May;241(9):986-95. doi: 10.1177/1535370216640943. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016. PMID: 27037279 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Ultrashort Pulse Laser Structuring of Metals on In-Vitro Cell Adhesion of Keratinocytes.J Funct Biomater. 2024 Jan 29;15(2):34. doi: 10.3390/jfb15020034. J Funct Biomater. 2024. PMID: 38391887 Free PMC article.
-
Aligned Nanotopography Promotes a Migratory State in Glioblastoma Multiforme Tumor Cells.Sci Rep. 2016 May 18;6:26143. doi: 10.1038/srep26143. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27189099 Free PMC article.
-
Early responses of vascular endothelial cells to topographic cues.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013 Aug 1;305(3):C290-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00264.2012. Epub 2013 May 22. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23703527 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrams GA, Goodman SL, Nealey PF, Franco M, Murphy CJ. Nanoscale topography of the basement membrane underlying the corneal epithelium of the rhesus macaque. Cell Tissue Res. 2000a;299:39–46. - PubMed
-
- Abrams GA, Schaus SS, Goodman SL, Nealey PF, Murphy CJ. Nanoscale topography of the corneal epithelial basement membrane and Descemet's membrane of the human. Cornea. 2000b;19:57–64. - PubMed
-
- Abrams GA, Bentley E, Nealey PF, Murphy CJ. Electron microscopy of the canine corneal basement membranes. Cells Tissues Organs. 2002;170:251–257. - PubMed
-
- Britland S, Morgan H, Wojiak-Stodart B, Riehle M, Curtis A, Wilkinson C. Synergistic and hierarchical adhesive and topographic guidance of BHK cells. Exp. Cell Res. 1996;228:313–325. - PubMed
-
- Burridge K, Chrzanowska-Wodnicka M. Focal adhesions, contractility, and signaling. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1996;12:463–519. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

