Minimal cis-acting elements required for adenovirus genome packaging
- PMID: 12692215
- PMCID: PMC153973
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.9.5127-5135.2003
Minimal cis-acting elements required for adenovirus genome packaging
Abstract
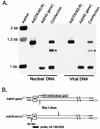
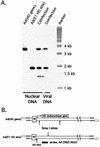
The design of drugs for treatment of virus infections and the exploitation of viruses as drugs for treatment of diseases could be made more successful by understanding the molecular mechanisms of virus-specific events. The process of assembly, and more specifically packaging of the genome into a capsid, is an obligatory step leading to future infections. To enhance our understanding of the molecular mechanism of packaging, it is necessary to characterize the viral components necessary for the event. In the case of adenovirus, sequences between nucleotides 200 and 400 at the left end of the genome are essential for packaging. This region contains a series of redundant bipartite sequences, termed A repeats, that function in packaging. Synthetic packaging sequences made of multimers of a single A repeat substitute for the authentic adenovirus packaging domain. A repeats are binding sites for the CCAAT displacement protein and the viral protein IVa2. Several lines of evidence implicate these proteins in the packaging process. It was not known, however, whether other cis-acting elements play a role in the packaging process as well. We utilized an in vivo approach to address the role of the inverted terminal repeats and the covalently linked terminal proteins in packaging of the adenovirus genome. Our results show that these elements are not necessary for efficient packaging of the viral genome. A significant implication of these results applicable to gene therapy vector design is that the linkage of the adenovirus packaging domain to heterologous DNA sequences should suffice for targeting to the viral capsid.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Functional interaction of the adenovirus IVa2 protein with adenovirus type 5 packaging sequences.J Virol. 2005 Mar;79(5):2831-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.5.2831-2838.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15709002 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular components interact with adenovirus type 5 minimal DNA packaging domains.J Virol. 1998 Aug;72(8):6339-47. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.8.6339-6347.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9658073 Free PMC article.
-
Binding of CCAAT displacement protein CDP to adenovirus packaging sequences.J Virol. 2003 Jun;77(11):6255-64. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.11.6255-6264.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12743282 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of adenovirus packaging.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2003;272:165-85. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-05597-7_6. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12747550 Review.
-
Mysteries of adenovirus packaging.J Virol. 2025 May 20;99(5):e0018025. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00180-25. Epub 2025 Apr 17. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 40243339 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Adenoviral L4 33K forms ring-like oligomers and stimulates ATPase activity of IVa2: implications in viral genome packaging.Front Microbiol. 2015 Apr 21;6:318. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00318. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25954255 Free PMC article.
-
Formation of a multiple protein complex on the adenovirus packaging sequence by the IVa2 protein.J Virol. 2007 Apr;81(7):3447-54. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02097-06. Epub 2007 Jan 17. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17229683 Free PMC article.
-
Presence of the adenovirus IVa2 protein at a single vertex of the mature virion.J Virol. 2008 Sep;82(18):9086-93. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01024-08. Epub 2008 Jul 9. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18614642 Free PMC article.
-
Components of Adenovirus Genome Packaging.Front Microbiol. 2016 Sep 23;7:1503. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01503. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27721809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic and bioinformatics analysis of HAdV-4, a human adenovirus causing acute respiratory disease: implications for gene therapy and vaccine vector development.J Virol. 2005 Feb;79(4):2559-72. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.4.2559-2572.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15681456 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banan, M., I. C. Rojas, W. H. Lee, H. L. King, J. V. Harriss, R. Kobayashi, C. F. Webb, and P. D. Gottlieb. 1997. Interaction of the nuclear matrix-associated region (MAR)-binding proteins, SATB1 and CDP/Cux, with a MAR element (L2a) in an upstream regulatory region of the mouse CD8a gene. J. Biol. Chem. 272:18440-18452. - PubMed
-
- Bridge, E., S. Medghalchi, S. Ubol, M. Leesong, and G. Ketner. 1993. Adenovirus early region 4 and viral DNA synthesis. Virology 193:794-801. - PubMed
-
- Carmo-Fonseca, M. 2002. The contribution of nuclear compartmentalization to gene regulation. Cell 108:513-521. - PubMed
-
- Cremer, T., and C. Cremer. 2001. Chromosome territories, nuclear architecture and gene regulation in mammalian cells. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2:292-301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

