The Papillomavirus E2 protein binds to and synergizes with C/EBP factors involved in keratinocyte differentiation
- PMID: 12692227
- PMCID: PMC153950
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.9.5253-5265.2003
The Papillomavirus E2 protein binds to and synergizes with C/EBP factors involved in keratinocyte differentiation
Abstract
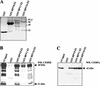
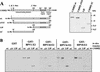
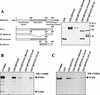
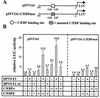
The papillomavirus life cycle is closely linked to the differentiation program of the host keratinocyte. Thus, late gene expression and viral maturation are restricted to terminally differentiated keratinocytes. A variety of cellular transcription factors including those of the C/EBP family are involved in the regulation of keratinocyte differentiation. In this study we show that the papillomavirus transcription factor E2 cooperates with C/EBPalpha and -beta in transcriptional activation. This synergism was independent of an E2 binding site. E2 and C/EBP factors synergistically transactivated a synthetic promoter construct containing classical C/EBPbeta sites and the C/EBPalpha-responsive proximal promoter of the involucrin gene, which is naturally expressed in differentiating keratinocytes. C/EBPalpha or -beta coprecipitated with E2 proteins derived from human papillomavirus type 8 (HPV8), HPV16, HPV18, and bovine papillomavirus type 1 in vitro and in vivo, indicating complex formation by the cellular and viral factors. The interaction domains could be mapped to the C terminus of E2 and amino acids 261 to 302 located within the bZIP motif of C/EBPbeta. Our data suggest that E2, via its interaction with C/EBP factors, may contribute to enhancing keratinocyte differentiation, which is suppressed by the viral oncoproteins E6 and E7 in HPV-induced lesions.
Figures
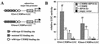

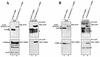
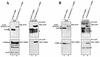
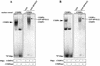
References
-
- Agarwal, C., T. Efimova, J. F. Welter, J. F. Crish, and R. L. Eckert. 1999. CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins. A role in regulation of human involucrin promoter response to phorbol ester. J. Biol. Chem. 274:6190-6194. - PubMed
-
- Crish, J. F., T. M. Zaim, and R. L. Eckert. 1998. The distal regulatory region of the human involucrin promoter is required for expression in epidermis. J. Biol. Chem. 273:30460-30465. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

