Disulfide bonding among micro 1 trimers in mammalian reovirus outer capsid: a late and reversible step in virion morphogenesis
- PMID: 12692241
- PMCID: PMC153963
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.9.5389-5400.2003
Disulfide bonding among micro 1 trimers in mammalian reovirus outer capsid: a late and reversible step in virion morphogenesis
Abstract
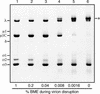
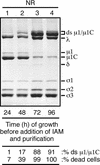
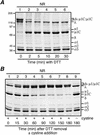
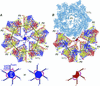
We examined how a particular type of intermolecular disulfide (ds) bond is formed in the capsid of a cytoplasmically replicating nonenveloped animal virus despite the normally reducing environment inside cells. The micro 1 protein, a major component of the mammalian reovirus outer capsid, has been implicated in penetration of the cellular membrane barrier during cell entry. A recent crystal structure determination supports past evidence that the basal oligomer of micro 1 is a trimer and that 200 of these trimers surround the core in the fenestrated T=13 outer capsid of virions. We found in this study that the predominant forms of micro 1 seen in gels after the nonreducing disruption of virions are ds-linked dimers. Cys679, near the carboxyl terminus of micro 1, was shown to form this ds bond with the Cys679 residue from another micro 1 subunit. The crystal structure in combination with a cryomicroscopy-derived electron density map of virions indicates that the two subunits that contribute a Cys679 residue to each ds bond must be from adjacent micro 1 trimers in the outer capsid, explaining the trimer-dimer paradox. Successful in vitro assembly of the outer capsid by a nonbonding mutant of micro 1 (Cys679 substituted by serine) confirmed the role of Cys679 and suggested that the ds bonds are not required for assembly. A correlation between micro 1-associated ds bond formation and cell death in experiments in which virions were purified from cells at different times postinfection indicated that the ds bonds form late in infection, after virions are exposed to more oxidizing conditions than those in healthy cells. The infectivity measurements of the virions with differing levels of ds-bonded micro 1 showed that these bonds are not required for infection in culture. The ds bonds in purified virions were susceptible to reduction and reformation in situ, consistent with their initial formation late in morphogenesis and suggesting that they may undergo reduction during the entry of reovirus particles into new cells.
Figures


References
-
- Aslund, F., and J. Beckwith. 1999. Bridge over troubled waters: sensing stress by disulfide bond formation. Cell 96:751-753. - PubMed
-
- Attoui, H., Q. Fang, F. M. Jaafar, J. F. Cantaloube, P. Biagini, P. De Micco, and X. De Lamballerie. 2002. Common evolutionary origin of aquareoviruses and orthoreoviruses revealed by genome characterization of Golden shiner reovirus, Grass carp reovirus, Striped bass reovirus and golden ide reovirus (genus Aquareovirus, family Reoviridae). J. Gen. Virol. 83:1941-1951. - PubMed
-
- Barton, E. S., J. L. Connolly, J. C. Forrest, J. D. Chappell, and T. S. Dermody. 2000. Utilization of sialic acid as a coreceptor enhances reovirus attachment by multi-step adhesion-strengthening. J. Biol. Chem. 276:2200-2211. - PubMed
-
- Barton, E. S., J. C. Forrest, J. L. Connolly, J. D. Chappell, Y. Liu, F. J. Schnell, A. Nusrat, C. A. Parkos, and T. S. Dermody. 2001. Junction adhesion molecule is a receptor for reovirus. Cell 104:441-451. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

